 |
 |
- Search
| J Stroke > Volume 25(3); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background and Purpose
We investigated the causal relationships between the gut microbiota (GM), stroke, and potential metabolite mediators using Mendelian randomization (MR).
Methods
We leveraged the summary statistics of GM (n=18,340 in the MiBioGen consortium), blood metabolites (n=115,078 in the UK Biobank), and stroke (cases n=60,176 and controls n=1,310,725 in the Global Biobank Meta-Analysis Initiative) from the largest genome-wide association studies to date. We performed bidirectional MR analyses to explore the causal relationships between the GM and stroke, and two mediation analyses, two-step MR and multivariable MR, to discover potential mediating metabolites.
Results
Ten taxa were causally associated with stroke, and stroke led to changes in 27 taxa. In the two-step MR, Bifidobacteriales order, Bifidobacteriaceae family, Desulfovibrio genus, apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1), phospholipids in high-density lipoprotein (HDL_PL), and the ratio of apolipoprotein B to ApoA1 (ApoB/ApoA1) were causally associated with stroke (all P<0.044). The causal associations between Bifidobacteriales order, Bifidobacteriaceae family and stroke were validated using the weighted median method in an independent cohort. The three GM taxa were all positively associated with ApoA1 and HDL_PL, whereas Desulfovibrio genus was negatively associated with ApoB/ApoA1 (all P<0.010). Additionally, the causal associations between the three GM taxa and ApoA1 remained significant after correcting for the false discovery rate (all q-values <0.027). Multivariable MR showed that the associations between Bifidobacteriales order, Bifidobacteriaceae family and stroke were mediated by ApoA1 and HDL_PL, each accounting for 6.5% (P=0.028) and 4.6% (P=0.033); the association between Desulfovibrio genus and stroke was mediated by ApoA1, HDL_PL, and ApoB/ApoA1, with mediated proportions of 7.6% (P=0.019), 4.2% (P=0.035), and 9.1% (P=0.013), respectively.
Stroke, one of the primary cardiovascular diseases, the second and third leading cause of death and disability worldwide, brings huge socioeconomic burdens [1,2]. Gut microbiota (GM), an emerging environmental factor contributing to human physiology and pathology [3], plays a pivotal role in the progression and outcome of stroke [4]. Mounting evidence suggests that stroke may lead to gut dysbiosis, whereas alterations in GM may determine stroke prognosis and recovery [5,6]. However, previous observational and preclinical studies have yielded largely inconsistent findings. For example, observational studies have shown that Prevotella and Faecalibacterium genera, which are among the human core microbiota, decreased in patients with an acute ischemic stroke or a transient ischemic attack [7], while they were reported to increase in patients with stroke in another case-control study [8]. An increase in Prevotella genus with a decrease in Faecalibacterium genus was found in monkey models with left middle cerebral artery occlusion [9], nevertheless, in mouse models, undergrowth of these two taxa was found three days after middle cerebral artery occlusion [10]. The causal relationship between GM and stroke, and the mechanism behind this relationship, remains unclear.
Interestingly, clinical and animal studies have shown that GM may affect stroke by modulating the blood levels of some bioactive metabolites, such as trimethylamine N-oxide and short-chain fatty acids [11]. Thus, we speculated that there might be causal associations between GM, metabolites, and stroke. Therefore, we sought to clarify these associations and identify potential metabolites that could be used for early diagnosis and as clinical treatment targets.
Mendelian randomization (MR), using genetic variants as instrumental variables (IVs), is a widely accepted method to control potential confounding factors [12], which can avoid reverse causation bias and allow more robust causal inferences between exposure and clinical outcomes. Furthermore, increasing evidence illustrates the value in using human genetic information of gut microbial features for clinical investigations [13], which enables us to employ MR as a methodology to infer causal relationships between the GM and stroke. We performed a bidirectional MR study and two mediation analyses using summary statistics from the largest and most up-to-date genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of the GM, blood metabolites, and stroke to dissect the associations between them.
Figure 1 illustrates the diagram of the study design and displays that the causal interpretation of MR estimates relies on three assumptions [12]. Specifically, the genetic variants used as IVs termed single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) should (1) strongly predict the exposures, (2) only associate with the outcome via the exposures, and (3) not associated with any confounder of the exposure-outcome association. The STROBE-MR (Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology using Mendelian Randomization) checklist was completed for this observational study (Appendix 1) [14].
Characteristics of corresponding GWAS data sources are described in Supplementary Table 1A [15-17]. Summary data of GM in the MiBioGen consortium (https://mibiogen.gcc.rug.nl) included 18,340 participants of multiple ancestries from 24 cohorts, of which 78% were Europeans [15]. An overview of the cohorts in MiBioGen are listed in Supplementary Table 1B. The MiBioGen consortium curated and analyzed genome-wide genotypes and the 16S fecal microbiome from participants. Only the taxa present in more than 10% of samples were used to identify genetic loci that affected relative abundance (microbiome quantitative trait loci), resulting in a total of 211 taxa: 131 genera, 35 families, 20 orders, 16 classes, and 9 phyla. Summary data of stroke in the Global Biobank Meta-analysis Initiative (GBMI) (https://www.globalbiobankmeta.org/resources) included 1,370,901 participants (60,176 cases and 1,310,725 controls) of multiple ancestries, of which 76% were Europeans [16]. The GBMI is a collaborative network of 19 biobanks from four continents representing more than 2.1 million consented individuals with genetic data linked to electronic health records. Stroke was defined using cohort-specific criteria: the Phecode, International Classification of Diseases codes, physician diagnosis or adjudication, or any available electronic health records. The detailed information is provided in Supplementary Table 1C. Based on phenotype-definition guidelines, the predominant form of stroke in the GBMI is ischemic stroke. Summary data of plasma-based metabolites in the UK Biobank (https://gwas.mrcieu.ac.uk) included an unprecedented sample size of up to 115,078 European participants [17]. The biomarkers span multiple metabolic pathways with proven relevance in the mechanisms of different diseases, including lipoprotein lipids in 14 subclasses, fatty acids and fatty acid compositions, as well as various low-molecular-weight metabolites, such as amino acids, ketone bodies, and glycolysis metabolites quantified in molar concentration units. Summary data were obtained from a GWAS of stroke in the UK Biobank (https://gwas.mrcieu.ac.uk/datasets/ukb-b-8714/)) as an independent validation cohort comprising 461,880 participants of European ancestry (7,055 cases and 454,825 controls).
For MR, it is important for the genetic variants used are representative of the microbiome features, thus we selected SNPs associated with GM at a more suggestive P-value of less than 1×10-5, as used in previous MR studies [13,18]. We selected SNPs associated with stroke and blood metabolites at conventional GWAS thresholds (P<5×10-8). Independent SNPs were then clumped to a linkage disequilibrium (LD) threshold of r2<0.001 at 1000 Genomes reference panel [19]. However, when no shared SNPs were available between the exposure and outcome, proxies from the 1000 Genomes European reference panel (r2≥0.8) were added. We included SNPs whose effect allele frequency was >0.01 and excluded SNPs whose F-statistic was <10 (a measure of the strength of these IVs) to avoid weak instrumental bias [20].
We first conducted bidirectional MR analyses to explore the causal relationship between the GM and stroke. The conventional MR approach inverse-variance-weighted (IVW) method was used for effect estimates, which was reported in beta (β) value with standard error for the continuous outcome and odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) for the binary outcome; P< 0.05 were considered nominally significant. In brief, IVW meta-analyzed SNP-specific Wald estimates (SNP outcome estimate divided by SNP exposure estimate) using random effects to obtain a final estimate of the causal effect [21].
To show the genetic correlation between GM and stroke, we performed bivariate linkage disequilibrium score regression (LDSC) using GWAS summary statistics [22]. The bivariate LDSC method is based on the principle that genetic variants in LD are inherited together and are more likely to be associated with a trait or disease than non-LD variants. It estimates the genetic correlation between two traits by simultaneously regressing the LD score of each SNP against the effect size of the two traits.
We have utilized summary statistics of blood metabolites from 115,078 participants in the UK Biobank, covering 249 plasma measurements of lipids, fatty acids, and small molecules such as amino acids, ketones, and glycolysis metabolites. To discover potential novel metabolites as mediators between the GM and stroke, we first excluded classical lipids and lipoproteins from this panel, including seven cholesterols, four total lipids, and four triglycerides, since their relationships with the GM and roles in the development of ischemic stroke have been well discussed in previous studies [23-25]. We further excluded metabolites that were genetically highly related to, or subclasses of, the aforementioned classical lipids and lipoproteins, including four cholesteryl esters, four free cholesterol, 70 relative lipoprotein lipid concentrations, and 105 lipid concentrations and compositions measured in 14 lipoproteins. We also conducted a bivariate LDSC analysis of these metabolites to evaluate their genetic correlations. The results revealed high genetic correlations between lipid and lipoprotein metabolites. The inclusion of these highly genetically correlated metabolites in the mediation analysis deteriorates the detection power owing to excessive multi-correction tests. Thus, 51 metabolic biomarkers were kept in the final mediation analysis including 18 fatty acids, 10 amino acids, 5 choline metabolites, 4 ketone bodies, 4 glycolysis-related metabolites, 4 phospholipids, 3 apolipoproteins, 2 fluid balance measures, and one inflammation measure.
We adopted two mediation approaches, two-step Mendelian randomization (TSMR) [26] and multivariable Mendelian randomization (MVMR) [27], to decompose the direct and indirect effects of the GM and blood metabolites on stroke. The TSMR assumes no interaction between exposure and mediator. In addition to the basic effect estimates of GM on stroke (β1) obtained from the univariate MR analyses, two more estimates were calculated: (1) the causal effect of the mediator (51 blood metabolites) on stroke (β2), and (2) the causal effect of the exposure (10 significant taxa on stroke in primary MR analysis) on the mediator (α). All IVW results were corrected for multiple testing using the false discovery rate (FDR) method, and the FDR q-values are provided. We also validated the primary findings of the TSMR in an independent cohort from the UK Biobank.
Finally, we performed MVMR as another method to validate the roles of the metabolites uncovered in TSMR. In MVMR, the controlled direct effect of the exposure on the outcome is estimated, which refers to the effect of metabolites on stroke adjusting for bacteria (β2*), and the effect of bacteria on stroke adjusting for metabolites (β1*) in our study [28]. The indirect effect, which refers to the causal effect of GM on stroke via mediators, can then be estimated using the product of coefficients method (α×β2*). Thus, the proportion mediated could be calculated as “indirect effect/total effect” ([α×β2*]/β1).
Up to four MR methods (MR-Egger, weighted median, simple mode, and weighted mode) that make differing pleiotropy assumptions have been used to generate effect estimates as sensitivity analyses [29,30]. We assessed horizontal pleiotropy using the MR-Egger method, which performs weighted linear regression with the intercept unconstrained [29]. The intercept represents the average pleiotropic effect across the genetic variants (the average direct effect of a variant with the outcome). If the intercept differed from zero (MR-Egger intercept P-value <0.05), there was evidence of horizontal pleiotropy. We also assessed heterogeneity using Cochrane’s Q test (smaller P-values indicate higher heterogeneity and higher potential for directional pleiotropy) and used leave-one-out analyses to detect SNP outliers.
All MR analyses were conducted in R (version 4.1.2; R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) using the “TwoSampleMR,” “tidyverse,” “ggplot2,” “purrr,” “data.table,” and “LDlinkR” packages [30]. FDR q-values were estimated using the R package “p.adjust.” [31] LDSC was based on LDSC software in Python (version 3.10.5; https://www.python.org/) [22].
The number of SNPs used as IVs ranged from 4 to 26 (median, 13) for the 211 GM taxa in the MiBioGen consortium, 7 to 72 (median, 35) for the 51 metabolites in the UK Biobank, and 13 for stroke in the GBMI (Supplementary Table 2-4). The median Fstatistic was 21.0 (ranged from 14.6 to 88.4) for GM and 52.2 (ranged from 23.8 to 16,413.1) for metabolites; an F-statistic >10 is considered sufficiently informative for MR analyses.
When evaluating the causal effects of GM on stroke, one order, one family, and six genera were negatively associated with stroke, whereas two genera were positively associated with stroke using the IVW method (Figure 2A and Supplementary Table 5). In these significant taxa, the Bifidobacteriales order and Bifidobacteriaceae family belonged to the Actinobacteria phylum, Desulfovibrio genus belonged to the Proteobacteria phylum, and the other seven taxa belonged to the Firmicutes phylum, among which Blautia genus demonstrated the most potent effect on the risk of stroke (OR 1.151, 95% CI, 1.057-1.254; P=0.001).
When evaluating the causal effects of stroke on the GM, the relative abundance of most of the significant taxa decreased after stroke, including four phyla, four classes, four orders, five families, and seven genera, whereas only three significant genera increased after stroke (Figure 2B and Supplementary Table 6). The reduced taxa belonging to the same phylum demonstrated similar effect sizes, among which Lentisphaerae phylum was the most affected by stroke (OR 0.623, 95% CI, 0.452-0.860; P=0.004). Furthermore, these results were deemed reliable without pleiotropy through a sensitivity analysis (Supplementary Table 7).
Bivariate LDSC analysis identified a strong negative genetic correlation between two genera and stroke: ChristensenellaceaeR.7group genus (Rg=-0.4074, P=0.031) and LachnospiraceaeFCS020group genus (Rg=-0.3576, P=0.046) (Supplementary Table 8).
In the TSMR (Figure 3), only four blood metabolites were causally associated with stroke (Table 1). Apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1; OR 0.906, 95% CI 0.857 to 0.957, P=0.0004) and phospholipids in high-density lipoproteins (HDL_PL; OR 0.931, 95% CI 0.882 to 0.984, P=0.011) were negatively associated with stroke, while the ratios of apolipoprotein B to ApoA1 (ApoB/ApoA1; OR 1.109, 95% CI 1.033 to 1.190, P=0.004) and tyrosine (OR 1.080, 95% CI 1.003 to 1.162, P=0.041) were positively associated with stroke. The IVW results for ApoA1 survived multiple testing corrections (FDR q-value=0.022). Among the 10 taxa that were causally associated with stroke, four were significantly associated with the above four metabolites (Table 2). Furthermore, all IVW results for associations between the four GM taxa and the four metabolites except ApoB/ApoA1 survived multiple testing corrections (FDR q-value <0.027). The FDR q-value for association between Desulfovibrio genus and ApoB/ApoA1 is 0.039 (Supplementary Table 9). Desulfovibrio genus, a protective taxon against stroke (OR 0.932, 95% CI 0.875-0.992, P=0.028), increased ApoA1 and HDL_PL, and decreased ApoB/ApoA1. Bifidobacteriales order and Bifidobacteriaceae family also exerted protective effects against stroke (both ORs 0.938, 95% CI, 0.882-0.998; P=0.044) by upregulating ApoA1 and HDL_PL and downregulating tyrosine. Blautia genus exerts detrimental effects on stroke by increasing tyrosine levels. The Q-statistics of both the IVW test and MR-Egger regression indicated no notable heterogeneity (P-values between 0.135 and 0.892). The P-values of the MR-Egger intercepts were between 0.062 and 0.933, suggesting minimal horizontal pleiotropy (Table 2). The results of the other sensitivity analyses are presented in Supplementary Table 9 and 10, and the pleiotropy test is presented in Supplementary Table 7. The bivariate LDSC results for the metabolites are provided in Supplementary Table 11. To validate the main findings of our present study, we conducted a two-sample MR analysis of significant GM taxa after FDR correction (Bifidobacteriales order, Bifidobacteriaceae family, and Desulfovibrio genus) using summary statistics of stroke GWAS in an independent cohort from the UK Biobank. The results are shown in Supplementary Table 12. Although the IVW method did not indicate the significance of any taxon, the weighted median method provided evidence supporting the effects of Bifidobacteriales order and Bifidobacteriaceae family on stroke. Moreover, all three GM taxa demonstrated consistent protective effects against stroke, confirming and strengthening the credibility of our findings.
We performed MVMR to validate the mediating effects of blood metabolites uncovered in TSMR. We calculated the indirect effect and proportion mediated by these metabolites, and found that the roles of ApoA1, HDL_PL, and ApoB/ApoA1 remained significant after adjusting for GM (Table 3). Overall, we observed indirect effects of ApoA1 and HDL_PL in associations between Bifidobacteriales order, Bifidobacteriaceae family and stroke, with a mediated proportion of 6.5% (P=0.028) and 4.6% (P= 0.033); and ApoA1, HDL_PL and ApoB/ApoA1 in association between Desulfovibrio genus and stroke with a mediated proportion of 7.6% (P=0.019), 4.2% (P=0.035), and 9.1% (P=0.013), respectively. The effect of tyrosine was insignificant after adjusting for the GM.
In the present large-scale MR study, 10 GM taxa were causally associated with stroke, and stroke affected the relative abundances of 27 taxa. Regarding a possible underlying mechanism, we uncovered three blood metabolites associated with the three GM taxa and stroke using TSMR and MVMR as mediation analyses. We suggest that Bifidobacteriales order, Bifidobacteriaceae family, and Desulfovibrio genus exert their protective effects against stroke by increasing ApoA1.
Blautia genus has a positive causal effect on stroke and demonstrated the most potent effect in our study. A previous clinical study also found that the Blautia genus increased significantly in acute ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack groups [32]. Desulfovibrio genus was negatively associated with stroke in our results, and one study which analyzed data from the Guangdong Gut Microbiome Project indirectly supported this association [33]. In this large-scale cohort study, Desulfovibrio genus was positively correlated with beneficial genera (Coprococcus, Ruminococcus, Akkermansia, and Faecalibacterium). It is worth noticing that Coprococcus1 genus and Ruminococcusgauvreauiigroup genus were negatively correlated with stroke in our results. Thus, Desulfovibrio genus may contribute to host health and the prevention of related diseases by co-occurring with other beneficial genera. Our findings also demonstrate that Bifidobacteriales order and Bifidobacteriaceae family are protective against stroke. Bifidobacterium genus is well known to have beneficial health effects, and several members are included in probiotics [34]. One study on Finnish men displayed that intake of fermented dairy products, which contain lactic acid bacteria such as Bifidobacteria and their primary metabolites (lactic acid), was inversely associated with the risk of coronary heart disease [35]. However, Butyricicoccus genus, a risk factor for stroke in our findings, was decreased in cerebral infarction patients, but the results were not convincing in this study considering the small sample size (79 cases and 98 healthy controls) [36].
In our study, stroke causally decreased the most significant GM taxa, whereas only three genera (Bilophila, Barnesiella, and Lachnoclostridium) increased after stroke. These results were consistent with most clinical studies [8,37,38]. Bilophila genus was found to be significantly enriched in patients with acute cerebral infarction [8] and Barnesiella genus and Lachnoclostridium genus were significantly elevated in subacute and chronic post-stroke patients, respectively [38]. Some inconsistent results, decreased Lachnoclostridium genus in cerebral infarction patients [36], were noted in a previous study. However, a single-center case-control study with relatively few participants may have major limitations in determining the causal relationship between GM and stroke.
Our MR study provides genetic evidence that several specific blood metabolites mediate the causal effects of the GM on stroke. In contrast to well-known biomarkers (such as trimethylamine N-oxide and short-chain fatty acids), our findings highlight the causal roles of apolipoproteins and phospholipids in cholesterol. In our MR analysis, higher serum levels of ApoA1 and HDL_PL were associated with a lower risk of stroke, in contrast to ApoB/ApoA1. A large international epidemiologic stroke study (INTERSTROKE) demonstrated that high serum ApoB/ApoA1 was associated with a higher risk of stroke [39]. Coincidentally, another study found that a low concentration of HDL_PL (particularly lysophospholipids) was present in acute coronary syndrome compared to stable coronary artery disease [40].
Our mediation analyses also provided genetic evidence for an association between GM and blood metabolites. To the best of our knowledge, no prior research has directly linked the Bifidobacteriales order, Bifidobacteriaceae family, or Desulfovibrio genus with ApoA1. However, some studies have assessed the potential relationship between GM richness, or their components, and apolipoproteins. For example, a large-scale observational study in Koreans (n=1,141) identified a significant increase in GM richness in subjects with low levels of ApoA1, suggesting that ApoA1 deficiency-driven microbial dysbiosis can contribute to inflammation or predispose to atherosclerosis development [41]. Another previous study found that activation of toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5) by certain bacterial components (flagellin) can increase the production of ApoA1 in the liver in mouse models [42]. Stimulation of ApoA1 production was also seen in human ApoA1-transgenic mice treated with oral flagellin. In brief, their findings suggest that commensal flagellated bacteria in the gut can modulate liver function and facilitate ApoA1 production through TLR5-mediated pathways. These findings, along with the results of our study, provide insights into the causal relationship between the GM and the regulation of lipid metabolism, particularly regarding distinct classes of apolipoproteins. Such information highlights the potential of targeted modulation of the GM as a strategy for improving cardiovascular health and warrants further exploration of the interplay between the GM, stroke, and apolipoprotein regulation in future studies.
The strengths of our study include utilization of the largest and latest GWASs of summary data for GM and stroke; the sample size of blood metabolites was over 110,000 participants [15-17], which guaranteed the statistical power of the findings. Stroke in GBMI included individuals of multi-ancestries from Biobank Japan (22,664 cases and 152,022 controls), FinnGen (18,661 cases and 162,201 controls), UK Biobank (1,958 cases and 407,633 controls), and other large consortiums (BioMe, BioVU, Estonian Biobank, Trøndelag Health Study, and Mass General Brigham Biobank) from all over the world. GM in MiBioGen also included individuals from the Netherlands (3,782 samples), Germany (3,582 samples, which covered three out of five cohorts in another single-country GWAS of microbial traits) [43], Denmark (2,776 samples), Belgium (2,259 samples in the Flemish Gut Flora Project), and other consortiums around the world. Additionally, we used two methods (TSMR and MVMR) for mediation analyses, and both supported the roles of ApoA1, HDL_PL, and ApoB/ApoA1 in the pathway of GM to stroke.
However, this study had several limitations. First, the characterization of microbiome profiles in the MiBioGen consortium uses 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing, which only allows resolution from the genus to phylum. Metagenomic sequencing provides more detail on a specific species level. However, a previous MR study of the GM found that the P-values were sometimes more significant for higher taxonomic units, such as genera or phyla, suggesting similar functions contributed by species [18]. Second, we reported the nominally significant GM taxa that were causally associated with stroke. Considering the complex interactions and interdependence among GM taxa [44] and the exploratory perspective of the current study design, multiple correction tests conducted within the overall number of taxa may be excessive and inappropriate for interpreting the results. Hence, nominally significant causal associations with relatively high FDR cannot completely negate the possibility of a relationship between GM and stroke. In fact, several GM taxa with nominal significance identified in our study have been supported by previous research findings [32-35]. Notably, the causal associations of Bifidobacteriales order and Bifidobacteriaceae family with stroke were statistically significant using both the IVW and weighted median methods in our study. More importantly, we validated their effects on stroke in an independent cohort and obtained consistent results, lending further support to our primary findings. Third, whether our findings apply to specific ethnic groups needs to be ascertained, given that over 70% of the study population was of European ancestry; differences exist in lifestyle, host metabolism, and resident GM among humans worldwide. The unequal distribution of genetic variants across different ethnic or racial groups can lead to population stratification, which may bias the study results [45]. From this perspective, the generalizability of the findings to other ethnic or racial groups should be interpreted with caution. It is crucial for future studies to incorporate a more diverse population to improve the generalizability of the results. Finally, MR assumes a linear relationship between exposure and outcome, but the relationship may be more complex in reality, involving nonlinear relationships and interactions with other environmental and genetic factors [45]. For example, some genetic variants may have a stronger effect on the outcome at higher or lower levels of exposure, or the effect of the exposure on the outcome may be mediated or moderated by other factors. Therefore, careful consideration of the potential nonlinear and interaction effects between the GM and stroke is warranted in future MR studies.
To our knowledge, this is the first study to comprehensively assess the causal relationships between the GM, blood metabolites, and stroke. These findings highlight the importance of elucidating the underlying mechanisms between the GM and stroke. These results provide novel insights into microbiome-based therapies and metabolite-targeted interventions for stroke.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary materials related to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2023.00381.
Supplementary Table 1A,B,C.
Characteristics of summary genome-wide association studies.
Overview of cohorts in MiBioGen
Overview of the definitions of stroke in cohorts in GBMI
Supplementary Table 2.
Used instrumental variables for 211 gut microbiota taxa from MiBioGen
Supplementary Table 3.
Used instrumental variables for stroke from Global Biobank Meta-Analysis Initiative
Supplementary Table 4.
Used instrumental variables for 51 blood metabolites from UK Biobank
Supplementary Table 5.
Five Mendelian randomization models estimate the causal effects of gut microbiota on stroke
Supplementary Table 6.
Five Mendelian randomization models estimate the causal effects of stroke on gut microbiota
Supplementary Table 7.
Pleiotropy of all Mendelian randomization results
Supplementary Table 8.
Linkage-disequilibrium score regression results between gut microbiota and stroke
Supplementary Table 9.
Five Mendelian randomization models estimate the causal effects of gut microbiota on blood metabolites
Supplementary Table 10.
Five Mendelian randomization models estimate the causal effects of 51 blood metabolites on stroke
Supplementary Table 11.
Linkage-disequilibrium score regression results among metabolites
Supplementary Table 12.
Validation of the causal effects of three gut microbiota taxa on stroke
Notes
Funding statement
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82270859, 81930021, 81970728, 91857205, 82088102, and 82022011), Shanghai Municipal Education Commission-Gaofeng Clinical Medicine Grant Support (20152508 Round 2), Shanghai Shenkang Hospital Development Center (SHDC12019101, SHDC2020CR1001A, and SHDC2020CR3069B), Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine (DLY201801), and Ruijin Hospital (2018CR002). MX, ML, TW, YX, JL, YB, WW, and GN are members of innovative research teams at high-level local universities in Shanghai.
Author contribution
Conceptualization: QW, HD, TH, MX. Study design: QW, HD, TH, MX. Methodology: QW, HD, TH. Data collection: all authors. Investigation: all authors. Statistical analysis: QW, HD, TH. Writing— original draft: QW, HD, TH. Writing—review & editing: all authors. Funding acquisition: MX, YB, WW, GN. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Acknowledgments
This work was made possible by the generous sharing of GWAS summary statistics from the MiBioGen consortium, Global Biobank Meta-Analysis Initiative, and UK Biobank. We thank all the individual patients who provided the sample that made the data available and all the investigators who provided these data to support this study.
Figure 1.
Assumptions and design of the bidirectional and mediation Mendelian randomization (MR) analyses. Firstly, a two-sample bidirectional MR was performed to investigate the causal relationships between gut microbiota (exposure) and stroke (outcome). Secondly, 51 blood metabolites (mediator) were selected for subsequent mediation analyses. Finally, a two-step MR analysis was conducted to detect potential mediating metabolites (Step 1, the effect of gut microbiota on metabolites; Step 2, the effect of metabolites on stroke), followed by a validation analysis using multivariable MR. GBMI, Global Biobank Meta-analysis Initiative. The images for gut microbiota, blood metabolites, and stroke were adapted from emojipng.com under the terms of the Non-Commercial Use License.

Figure 2.
Mendelian randomization analyses show causal effects between gut microbiota and stroke. (A) The causal effect of gut microbiota on stroke. (B) The causal effect of stroke on gut microbiota. The dots colored in red and green indicate positive and negative odds ratios respectively from the inverse-varianceweighted analysis (truncated at P-value <0.05). CI indicates confidence intervals and prefix “p_/c_/o_/f_/g_” represents phylum/class/order/family/genus, respectively. Taxonomy with the same background color belongs to the same phylum.
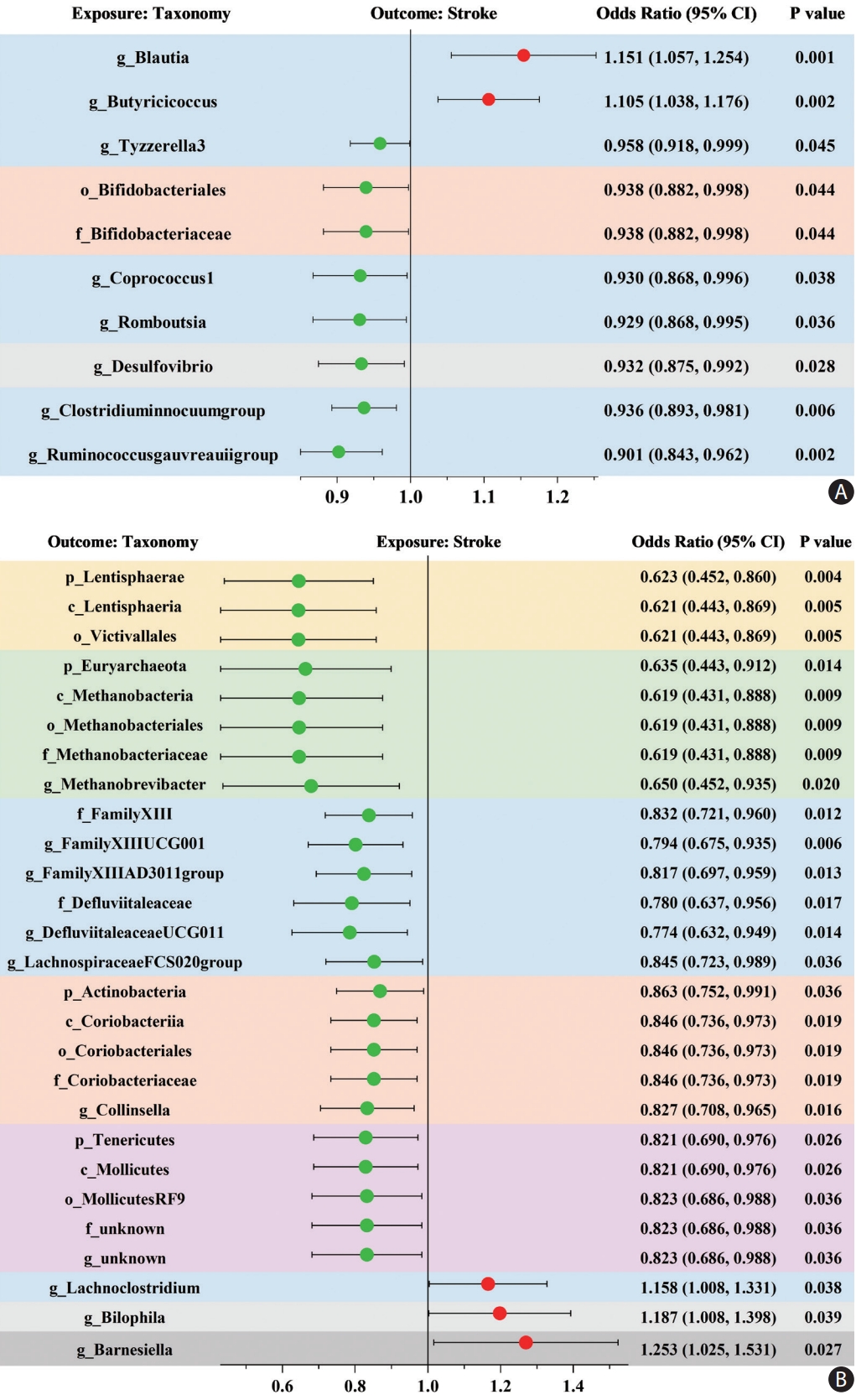
Figure 3.
Mendelian randomization analyses show causal effects of blood metabolites on gut microbiota and stroke. The diagram displays the mediation mode of “gut microbiota-blood metabolites-stroke” in two-step Mendelian randomization. Beta values (β) indicate the causal effect estimates using the inverse- variance-weighted method (truncated at P<0.05). Characters colored in red and green signify positive and negative associations, respectively. HDL_PL, phospholipids in high-density lipoprotein; ApoA1, apolipoprotein A1; ApoB/ApoA1, the ratio of apolipoprotein B to apolipoprotein A1.

Table 1.
Mendelian randomization analyses of the causal effects between blood metabolites and stroke
Odds ratios, 95% CI, and P-values were obtained from Mendelian randomization analysis. The heterogeneity test in the IVW method was performed using Cochran’s Q statistic.
SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; CI, confidence interval; Ph, P-value for heterogeneity; Pintercept, P-value for the intercept of the MR-Egger regression; ApoA1, apolipoprotein A1; IVW, inverse-variance-weighted; MR, Mendelian randomization; HDL_PL, phospholipids in high-density lipoproteins; ApoB/ApoA1, ratio of apolipoprotein B to apolipoprotein A1.
Table 2.
Mendelian randomization analyses of the causal effects between gut microbiota and blood metabolites
Beta, standard errors (SE), and P-values were obtained from the Mendelian randomization analysis. The heterogeneity test in the IVW method was performed using Cochran’s Q statistic. The prefix “o_/f_/g_” represents order/family/genus respectively.
SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; Ph, P-value for heterogeneity; Pintercept, P-value for the intercept of the MR-Egger regression; ApoA1, apolipoprotein A1; IVW, inverse-variance-weighted; MR, Mendelian randomization; HDL_PL, phospholipids in high-density lipoproteins; ApoB/ApoA1, ratio of apolipoprotein B to apolipoprotein A1.
Table 3.
Multivariable Mendelian randomization analyses of the causal effects between gut microbiota, blood metabolites and stroke
Beta (β), standard errors (SE), and P-values were obtained from multivariable Mendelian randomization analysis. β1* and β2* represent the controlled direct effects of each pair of bacteria and metabolite on stroke after adjusting for each other. α is the causal effect of exposure on mediator; indirect effect (α×β2*) is the effect of exposure on stroke via corresponding mediator; β1 is the total effect of exposure on stroke; proportion mediated is calculated as the “indirect effect/total effect.” The prefix “o_/f_/g_” represents order/family/genus respectively.
ApoA1, apolipoprotein A1; HDL_PL, phospholipids in high-density lipoproteins; ApoB/ApoA1, ratio of apolipoprotein B to apolipoprotein A1.
References
1. Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Alonso A, Beaton AZ, Bittencourt MS, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2022 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022;145:e153-e639.


3. Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross J, Burcelin R, Gibson G, Jia W, et al. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 2012;336:1262-1267.


4. Honarpisheh P, Bryan RM, McCullough LD. Aging microbiotagut-brain axis in stroke risk and outcome. Circ Res 2022;130:1112-1144.



5. Xu K, Gao X, Xia G, Chen M, Zeng N, Wang S, et al. Rapid gut dysbiosis induced by stroke exacerbates brain infarction in turn. Gut 2021;70:1486-1494.

6. Winek K, Dirnagl U, Meisel A. Role of the gut microbiota in ischemic stroke. Neurol Int Open 2017;1:E287-E293.

7. Yin J, Liao SX, He Y, Wang S, Xia GH, Liu FT, et al. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota with reduced trimethylamine-N-oxide level in patients with large-artery atherosclerotic stroke or transient ischemic attack. J Am Heart Assoc 2015;4:e002699.



8. Xia GH, You C, Gao XX, Zeng XL, Zhu JJ, Xu KY, et al. Stroke dysbiosis index (SDI) in gut microbiome are associated with brain injury and prognosis of stroke. Front Neurol 2019;10:397.



9. Chen Y, Liang J, Ouyang F, Chen X, Lu T, Jiang Z, et al. Persistence of gut microbiota dysbiosis and chronic systemic inflammation after cerebral infarction in cynomolgus monkeys. Front Neurol 2019;10:661.



10. Singh V, Roth S, Llovera G, Sadler R, Garzetti D, Stecher B, et al. Microbiota dysbiosis controls the neuroinflammatory response after stroke. J Neurosci 2016;36:7428-7440.



11. Peh A, O’Donnell JA, Broughton BRS, Marques FZ. Gut microbiota and their metabolites in stroke: a double-edged sword. Stroke 2022;53:1788-1801.


12. Lawlor DA, Harbord RM, Sterne JA, Timpson N, Davey Smith G. Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat Med 2008;27:1133-1163.


13. Sanna S, van Zuydam NR, Mahajan A, Kurilshikov A, Vich Vila A, Võsa U, et al. Causal relationships among the gut microbiome, short-chain fatty acids and metabolic diseases. Nat Genet 2019;51:600-605.




14. Skrivankova VW, Richmond RC, Woolf BAR, Yarmolinsky J, Davies NM, Swanson SA, et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using Mendelian randomization: the STROBE-MR statement. JAMA 2021;326:1614-1621.


15. Kurilshikov A, Medina-Gomez C, Bacigalupe R, Radjabzadeh D, Wang J, Demirkan A, et al. Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition. Nat Genet 2021;53:156-165.


16. Zhou W, Kanai M, Wu KH, Rasheed H, Tsuo K, Hirbo JB, et al. Global Biobank Meta-analysis Initiative: powering genetic discovery across human disease. Cell Genom 2022;2:100192.


17. Julkunen H, Cichon´ska A, Tiainen M, Koskela H, Nybo K, Mäkelä V, et al. Atlas of plasma NMR biomarkers for health and disease in 118,461 individuals from the UK Biobank. Nat Commun 2023;14:604.




18. Liu X, Tong X, Zou Y, Lin X, Zhao H, Tian L, et al. Mendelian randomization analyses support causal relationships between blood metabolites and the gut microbiome. Nat Genet 2022;54:52-61.



19. Sudmant PH, Rausch T, Gardner EJ, Handsaker RE, Abyzov A, Huddleston J, et al. An integrated map of structural variation in 2,504 human genomes. Nature 2015;526:75-81.




20. Burgess S, Thompson SG; CRP CHD Genetics Collaboration. Avoiding bias from weak instruments in Mendelian randomization studies. Int J Epidemiol 2011;40:755-764.


21. Burgess S, Small DS, Thompson SG. A review of instrumental variable estimators for Mendelian randomization. Stat Methods Med Res 2017;26:2333-2355.




22. Bulik-Sullivan BK, Loh PR, Finucane HK, Ripke S, Yang J, Patterson N, et al. LD score regression distinguishes confounding from polygenicity in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 2015;47:291-295.




23. Jia J, Dou P, Gao M, Kong X, Li C, Liu Z, et al. Assessment of causal direction between gut microbiota-dependent metabolites and cardiometabolic health: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis. Diabetes 2019;68:1747-1755.



24. Fu J, Bonder MJ, Cenit MC, Tigchelaar EF, Maatman A, Dekens JA, et al. The gut microbiome contributes to a substantial proportion of the variation in blood lipids. Circ Res 2015;117:817-824.



25. Hindy G, Engström G, Larsson SC, Traylor M, Markus HS, Melander O, et al. Role of blood lipids in the development of ischemic stroke and its subtypes: a Mendelian randomization study. Stroke 2018;49:820-827.



26. Burgess S, Daniel RM, Butterworth AS, Thompson SG; EPIC-InterAct Consortium. Network Mendelian randomization: using genetic variants as instrumental variables to investigate mediation in causal pathways. Int J Epidemiol 2015;44:484-495.



27. Sanderson E. Multivariable Mendelian randomization and mediation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2021;11:a038984.



28. Burgess S, Thompson SG. Multivariable Mendelian randomization: the use of pleiotropic genetic variants to estimate causal effects. Am J Epidemiol 2015;181:251-260.



29. Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Burgess S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol 2015;44:512-525.



30. Hemani G, Zheng J, Elsworth B, Wade KH, Haberland V, Baird D, et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife 2018;7:e34408.




31. Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Series B (Methodol) 1995;57:289-300.


32. Xu N, Kan P, Yao X, Yang P, Wang J, Xiang L, et al. Astragaloside IV reversed the autophagy and oxidative stress induced by the intestinal microbiota of AIS in mice. J Microbiol 2018;56:838-846.



33. Chen YR, Jing QL, Chen FL, Zheng H, Chen LD, Yang ZC. Desulfovibrio is not always associated with adverse health effects in the Guangdong Gut Microbiome Project. PeerJ 2021;9:e12033.




35. Koskinen TT, Virtanen HEK, Voutilainen S, Tuomainen TP, Mursu J, Virtanen JK. Intake of fermented and non-fermented dairy products and risk of incident CHD: the Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study. Br J Nutr 2018;120:1288-1297.


36. Li H, Zhang X, Pan D, Liu Y, Yan X, Tang Y, et al. Dysbiosis characteristics of gut microbiota in cerebral infarction patients. Transl Neurosci 2020;11:124-133.



37. Liu Y, Kong C, Gong L, Zhang X, Zhu Y, Wang H, et al. The association of post-stroke cognitive impairment and gut microbiota and its corresponding metabolites. J Alzheimers Dis 2020;73:1455-1466.


38. Dang Y, Zhang X, Zheng Y, Yu B, Pan D, Jiang X, et al. Distinctive gut microbiota alteration is associated with poststroke functional recovery: results from a prospective cohort study. Neural Plast 2021;2021:1469339.




39. O’Donnell MJ, Chin SL, Rangarajan S, Xavier D, Liu L, Zhang H, et al. Global and regional effects of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with acute stroke in 32 countries (INTERSTROKE): a case-control study. Lancet 2016;388:761-775.


40. Meikle PJ, Formosa MF, Mellett NA, Jayawardana KS, Giles C, Bertovic DA, et al. HDL phospholipids, but not cholesterol distinguish acute coronary syndrome from stable coronary artery disease. J Am Heart Assoc 2019;8:e011792.



41. Yun KE, Kim J, Kim MH, Park E, Kim HL, Chang Y, et al. Major lipids, apolipoproteins, and alterations of gut microbiota. J Clin Med 2020;9:1589.



42. Yiu JHC, Chan KS, Cheung J, Li J, Liu Y, Wang Y, et al. Gut microbiota-associated activation of TLR5 induces apolipoprotein A1 production in the liver. Circ Res 2020;127:1236-1252.



43. Rühlemann MC, Hermes BM, Bang C, Doms S, Moitinho-Silva L, Thingholm LB, et al. Genome-wide association study in 8,956 German individuals identifies influence of ABO histo-blood groups on gut microbiome. Nat Genet 2021;53:147-155.



- TOOLS