 |
 |
- Search
| J Stroke > Volume 21(3); 2019 > Article |
|
Functional outcome after thrombectomy in patients with acute ischemic stroke still varies significantly. Higher blood glucose levels (BGL) have been associated with poor clinical outcome, but the pathophysiological causes are not yet understood. Prior animal studies suggested that hyperglycemia accelerates the transformation of ischemic penumbra into infarction resulting in larger infarcts [1]. Moreover, altered blood-brain barrier permeability or increased lactic acid production in the ischemic tissue have been discussed as potential pathophysiological causes [2]. Recently, higher blood glucose has been described as an important predictor for early cerebral brain edema; however, in the referred study, edema was only determined using a visual three-step approach, which primarily assessed infarct size [3]. Nonetheless, this study introduced early brain edema as a possible factor resulting from elevated BGL, whose pathophysiology is not yet entirely understood.
The purpose of this pilot study was to investigate the relationship of admission blood glucose and early cerebral edema in stroke patients using a quantitative computed tomography (CT) based method to determine ischemic lesion water uptake [4].
We retrospectively screened all ischemic stroke patients with large vessel occlusion of the middle cerebral artery territory admitted between February 2015 and March 2018 at the local high-volume tertiary stroke center. The a priori defined inclusion criteria can be found in the Supplementary Material. Baseline clinical characteristics and demographic information were extracted from the medical records, including time from onset to admission and blood glucose at admission, as well as anti-diabetic medication including insulin. A history of diabetes mellitus was retrieved from clinical documentation. Functional outcome was extracted from the registry using modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores after 90 days. We used a standardized procedure to quantify early net lesion water uptake (NWU) in the ischemic core lesion at the time of admission imaging as reported elsewhere [5-7]. The relationship of BGL and early edema (e.g., NWU in admission CT) was analyzed using multivariable linear regression adjusted for Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS), age, and National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS). The association of BGL on clinical outcome was analyzed using univariable and multivariable logistic regression analysis with backward selection adjusted for age, NIHSS, ASPECTS, NWU, and recanalization status. Details on statistical analyses can be found in the Supplementary Material.
In this pilot study, 165 patients fulfilled all inclusion criteria and were analyzed (Table 1). The median age was 76 (interquartile range [IQR], 65 to 82) and 69 patients (42%) were women. In 30 patients, a known history of diabetes mellitus type 2 was found in medical documentation (18%). In these patients, the mean BGL at admission was significantly higher (157 mg/dL vs. 127 mg/dL, P<0.0001). Regarding existing diabetes medication, eight patients had subcutaneous insulin in their medication list, five patients with metformin, four patients with gliptins, and one patient with sulfonylurea. The mean±standard deviation (SD) time from symptom onset to admission imaging was 3.1±1.8 hours and the median NIHSS was 16 (IQR, 13 to 19). The median ASPECTS was 8 (IQR, 6 to 9). One hundred and thirty-one patients (79%) received successful endovascular recanalization with TICI 2b/3. Patients with a history of diabetes had no significant difference in early formation of ischemic edema than patients without (mean NWU 10.6% vs. 9.8%, P=0.44). When using BGL of 140 mg/dL as cut-off to distinguish two patient groups, however, we found significant differences when comparing these groups. The mean±SD NWU for patients with BGL <140 mg/dL was significantly lower than NWU in patients with BGL >140 mg/dL (112.3 mg/dL [15.2] vs. 171.1 mg/dL [33.8], P<0.0001). In multivariable linear regression analysis, the association of BGL on NWU was assessed adjusted for ASPECTS, NIHSS, and age. For every 10 mg/dL increase in BGL, NWU significantly increased by 0.56% (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.33 to 0.79; P<0.001) (Figure 1).
Univariate and multivariable logistic regression analysis was performed to predict good outcome (mRS 0 to 2) using BGL, NIHSS, age, NWU, recanalization status and ASPECTS as independent variables. Higher BGL significantly reduced the likelihood of good outcome of 3% per 1 mg/dL increase (odds ratio, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.96 to 0.99; P=0.0006) (Figure 2).
The aim of this pilot study was to investigate the relationship of admission blood glucose, early ischemic brain edema and clinical outcome in ischemic stroke patients. The main findings of this exploratory analysis was that increasing BGL was significantly associated with higher early brain edema and worse functional outcome assessed by mRS after 90 days. To our knowledge, the present pilot study is the first that investigated the relationship of BGL and early ischemic edema using a quantitative imaging biomarker [5]. A lately published paper observed that elevated BGL was an important predictor for early ischemic edema, but these findings were only based on visual rating primarily describing lesion size [3]. Our pilot study confirmed prior observations that higher levels of blood glucose were associated with reduced functional independence, adjusted for baseline clinical parameter and treatment. Early cerebral brain edema might be the link between elevated BGL and poor outcome. In the future, quantification of early ischemic edema might be used to monitor treatment effects of adjuvant anti-edematous treatment, such as glyburide [8]. It is important to realize that applying antidiabetic drugs or insulin in clinical trials did not improve functional outcome although animal studies often showed promising results [9]. Likewise, the use of further neuroprotectants for adjuvant stroke treatment often failed. In contrast to clinical trials, >80% of prior preclinical studies examined the neuroprotectant in animal models in combination with complete vessel reperfusion. Considering the low recanalization rates in patients with large vessel occlusion and intravenous lysis, the disappointing results of several clinical trials testing adjuvant treatment strategies may be recognizable. Therefore, future clinical trials could combine vessel reperfusion with neuroprotectants or anti-diabetic treatment in patients with hyperglycemia.
Limitations of this pilot study include the small number of patients due to strict inclusion and exclusion criteria. Furthermore, hyperglycemia is a dynamic process, and an isolated blood glucose value may not be sufficient to capture the whole complexity of ischemic brain. Finally, future studies should especially investigative the relationship between ischemic brain edema, BGL and collateral status as potential important mediator, as recently described [10].
In conclusion, this study confirms the association between higher levels of blood glucose and reduced likelihood of functional independence, adjusted for baseline clinical parameters and treatment. Early cerebral brain edema might be a link between elevated BGL and poor outcome.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary materials related to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2019.01935.
Acknowledgments
Jens Fiehler: Research support: German Ministry of Science and Education (BMBF and BMWi), German Research Foundation (DFG), European Union (EU), Hamburgische Investitions- und Förderbank (IFB), Medtronic, Microvention, Philips, Stryker, Consultant for: Acandis, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cerenovus, Covidien, Evasc Neurovascular, MD Clinicals, Medtronic, Medina, Microvention, Penumbra, Route92, Stryker, Transverse Medical. Götz Thomalla: Consultant for Acandis, Bayer Healthcare, Boehringer Ingelheim, BristolMyersSquibb/Pfizer, Covidien, Glaxo Smith Kline; lead investigator of the WAKE-UP study; Principal Investigator of the THRILL study; Grants by the European Union (Grant No. 278276 und 634809) and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 936, Projekt C2).
Figure 1.
Association of blood glucose with early net lesion water uptake (NWU). Association of blood glucose (x axis) with ischemic NWU (y axis) in the admission computed tomography. Shaded area indicates a 95% confidence interval.
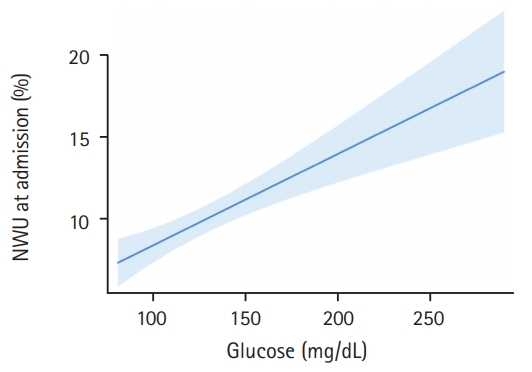
Figure 2.
Multivariable logistic regression analysis to display (A) the impact of admission blood glucose (mg/dL) (B) and early net lesion water uptake (NWU) at admission (%) on clinical outcome (probability for functional independence), adjusted for age, National Institute of Health Stroke Scale, and Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score. Shaded area indicates a 95% confidence interval. mRS, modified Rankin Scale.
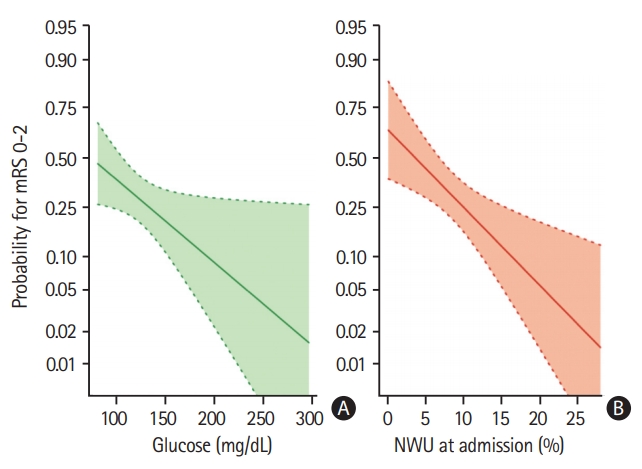
Table 1.
Patient characteristics
References
1. Martini SR, Kent TA. Hyperglycemia in acute ischemic stroke: a vascular perspective. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2007;27:435-451.


2. Lu G, Ren ZQ, Zhang JX, Zu QQ, Shi HB. Effects of diabetes mellitus and admission glucose in patients receiving mechanical thrombectomy: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Neurocrit Care 2018;29:426-434.



3. Thorén M, Azevedo E, Dawson J, Egido JA, Falcou A, Ford GA, et al. Predictors for cerebral edema in acute ischemic stroke treated with intravenous thrombolysis. Stroke 2017;48:2464-2471.


4. Broocks G, Flottmann F, Scheibel A, Aigner A, Faizy TD, Hanning U, et al. Quantitative lesion water uptake in acute stroke computed tomography is a predictor of malignant infarction. Stroke 2018;49:1906-1912.


5. Broocks G, Flottmann F, Ernst M, Faizy TD, Minnerup J, Siemonsen S, et al. Computed tomography-based imaging of voxel-wise lesion water uptake in ischemic brain: relationship between density and direct volumetry. Invest Radiol 2018;53:207-213.


6. Broocks G, Hanning U, Flottmann F, Schönfeld M, Faizy TD, Sporns P, et al. Clinical benefit of thrombectomy in stroke patients with low ASPECTS is mediated by oedema reduction. Brain 2019;142:1399-1407.



7. Minnerup J, Broocks G, Kalkoffen J, Langner S, Knauth M, Psychogios MN, et al. Computed tomography-based quantification of lesion water uptake identifies patients within 4.5 hours of stroke onset: a multicenter observational study. Ann Neurol 2016;80:924-934.


8. Sheth KN, Elm JJ, Molyneaux BJ, Hinson H, Beslow LA, Sze GK, et al. Safety and efficacy of intravenous glyburide on brain swelling after large hemispheric infarction (GAMESRP): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol 2016;15:1160-1169.


- TOOLS