 |
 |
- Search
| J Stroke > Volume 20(3); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Cerebral small vessel disease (cSVD) has a crucial role in lacunar stroke and brain hemorrhages and is a leading cause of cognitive decline and functional loss in elderly patients. Based on underlying pathophysiology, cSVD can be subdivided into amyloidal and non-amyloidal subtypes. Genetic factors of cSVD play a pivotal role in terms of unraveling molecular mechanism. An important pathophysiological mechanism of cSVD is blood-brain barrier leakage and endothelium dysfunction which gives a clue in identification of the disease through circulating biological markers. Detection of cSVD is routinely carried out by key neuroimaging markers including white matter hyperintensities, lacunes, small subcortical infarcts, perivascular spaces, cerebral microbleeds, and brain atrophy. Application of neural networking, machine learning and deep learning in image processing have increased significantly for correct severity of cSVD. A linkage between cSVD and other neurological disorder, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease and non-cerebral disease, has also been investigated recently. This review draws a broad picture of cSVD, aiming to inculcate new insights into its pathogenesis and biomarkers. It also focuses on the role of deep machine strategies and other dimensions of cSVD by linking it with several cerebral and non-cerebral diseases as well as recent advances in the field to achieve sensitive detection, effective prevention and disease management.
Cerebrovascular diseases remain a leading cause of death and functional disability worldwide. The global burden of disease 2013 study undertaken by American Heart Association identified greater stroke burden in men than women with 133/100,000 males-years and 99/100,000 females-years incidence of ischemic stroke [1]. According to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke, contributing to almost 87% of the incidences among total stroke incidence [2].
On the basis of different clinical pictures and the characteristic appearance of the lesion and coexisting vascular diseases, ischemic stroke is subclassified into lacunar, embolic, and thrombotic cerebral infarction [3]. Cerebral small vessel disease (cSVD) is a term used for different pathological processes that affect the small vessels of the brain, including small arteries, arterioles, capillaries, and small veins. cSVD has a crucial role in lacunar cerebral infarction and deep or cortical haemorrhages [4]. In addition to cognitive decline [5] and dementia [6], gait problems [7] are also frequently associated with cSVD.
Despite advances in the last decades in the field of neuroimaging and biomarkers, the pathogenesis of vascular disease is not well known. Damage to the blood-brain barrier (BBB) seems to be a common and early mechanism in the different forms of sporadic cSVD [8]. With the discovery of several subtypes of hereditary and forms different genetic, molecular, and cellular disease mechanisms has expanded the knowledge about the pathophysiology of this disease. We have thus divided the cSVD based upon two different aspects: (1) pathological cSVD and (2) genetic cSVD.
This review gives a comprehensive picture of small vessel disease (SVD) covering its pathological subtypes in sporadic and hereditary forms with special emphasis in the role of the BBB dysfunction in the initial pathogenesis. Moreover a complete description of the imaging markers, the development of automated methods for its detection and quantification and some unraveling relation to non-cerebral components is presented. Altogether, this review provides researchers to generate an in-depth understanding of cSVD, it will further aim towards exploring its prevention and treatment strategy.
The term cSVD is used with various meanings in different contexts. The topography of the underlying microvascular pathology is different in each case of cSVD. Additionally, to elucidate cellular and molecular mechanisms of hereditary forms of cSVD, it is important to understand genetics behind cSVD pathology. To describe a range of genetical and pathological features associated with cSVD, it is stratified in different subtypes here taking these two attributes (pathology and genetics).
Approximately one-fifth of symptomatic strokes are lacunar stroke syndromes [9], which are often the more severe (sometimes lethal) kind of strokes namely spontaneous parenchymal brain hemorrhage (PBH). These are associated with cSVD [10]. However, even though sporadic cSVD is the leading cause of PBH, the topography of the underlying microvascular pathology is different in each case. To provide some kind of a general framework, cSVD is categorized in two main forms. The first is the amyloidal form which includes cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), a chronic degenerative disease. The second form is characterized as non-amyloidal form of cSVD which is often related to common vascular risk factors, such as elderly age, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and many other factors [4].
CAA is a common amyloidal form of cSVD. Incidences of CAA are mostly associated with advanced age [11]. It is caused by a progressive deposition of β-amyloid in the walls of cortical and leptomeningeal small arteries, which leads to vessel dysfunction and brain parenchymal injury. Deposition of β-amyloid is thought to be involved in vascular occlusion and rupture. CAA related vasculopathy includes features such as fibrinoid necrosis, loss of smooth muscle cells, wall thickening, microaneurysm formation, and perivascular blood breakdown with the resulting product deposition [12-16].
Histological diagnosis of CAA requires use of special staining for amyloid under light microscopy. CAA now is not only a cerebrovascular pathological disorder, but also a clinical syndrome and has a distinct phenotype of neuroimaging and neuropathology. Multiple lobar cerebral microbleeds (CMBs) or cortical superficial siderosis shows peculiar CAA manifestations on neuroimaging [11]. Recently, the use of positron emission tomography (PET) with amyloid tracers has been used to label vascular β-amyloid in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) and might serve as a marker in future clinical trials [17].
Based on the specific location of amyloid deposition and allelic difference, at least two pathological subtypes of CAA have been identified: CAA type-1 characterized by amyloid in cortical capillaries, and CAA type-2, in which amyloid deposits are restricted to leptomeningeal and cortical arteries, but not capillaries [18]. Decreased cortical grey matter in the occipital lobe and decreased flux in the basilar artery were noted in patients of symptomatic hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis-Dutch type (HCHWA-D) [19]. The appearance of cortical thinning in patients with HCHWA-D indicated that vascular amyloid is an independent contributor to cortical atrophy. CAA-related cortical atrophy was facilitated by vascular dysfunction and even observed in the absence of Alzheimer’s disease [20]. Moreover, apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene polymorphism is associated with the two subtypes of CAA. APOE ε4 allele and APOE ε2 is legitimately associated with type-1 and type-2 diseases, respectively [15].
In contrast to CAA, less specific and more difficult to define form of cSVD is broadly termed as non-amyloidal SVD. The term ‘‘hypertensive arteriopathy’’ is widely used to describe this form of cSVD which is often related to many vascular risk factors like hypertension, diabetes, etc. However, the term ‘‘hypertensive arteriopathy’’ is somewhat misleading in terms that it is not always necessarily related specifically to hypertension (accounted for other risk factors). This form of cSVD has also been enormously termed arteriolosclerosis, age-related or vascular risk factor related cSVD, or degenerative microangiopathy in various other reports [4,21].
‘‘Hypertensive arteriopathy’’ can be further divided on the grounds of structural histopathological abnormalities, e.g., distal atherosclerosis, arteriolosclerosis, lipohyalinosis (‘‘mural disease’’), fibrinoid necrosis, and microaneurysms. These subdivisions differ in distribution in micro vessels size and can coexist in various combinations. It is difficult to differentiate hypertensive and non-hypertensive pathological changes. Fibrinoid necrosis, and sometimes microaneurysm formation, is more common in hypertensive patients’ brains than in those without hypertension which eventually lead to deep PBH [10,22]. Nevertheless there is no consensus on the microscopic characterization of small vessel changes of “hypertensive arteriopathy” so that its severity is difficult to evaluate in any given case. Later epidemiological studies of patients with small deep infarcts has shown that the prevalence of hypertension, being more common, seemed no different than the patients with large artery extracranial and intracranial occlusive disease, which raised doubt about the importance of hypertension in causing the vascular changes that leads to these small deep infarcts [23].
Collagens are components of the extracellular matrix and are found in the normal vascular wall, where they usually are weakly immunolabelled. Over expression of fibrillar collagen type-III as well as strong immunoreactivity of the basement membrane component collagen type-IV in vascular smooth muscle cells were marked to be associated with non-amyloid microangiopathy [24]. It has been associated with white matter hyperintensities (WMHs) [25], enlarged perivascular spaces (PVSs) in basal ganglia [26], lacunar infarcts [27], and ICH in the several previous literatures. Comparative evaluation is carried out for detailed understanding of these two forms of cSVD (Table 1).
Genetics may play an important role in elucidating the cellular and molecular mechanisms and thus the pathophysiology of hereditary forms of cSVD. Genetic factors and their pathways have been elaborated for cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL), cerebral autosomal recessive arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CARASIL), incontinentia pigmenti, and several other forms of cSVD. Sometimes, common denominators in monogenic SVD may contribute to disease progression. Even, distinct genetic mechanisms have been suggested in patients with lacunar stroke of different forms of cSVD [28]. Genetic studies are also important for elucidation of pathways involved and their interrelationship with other diseases involving brain’s white matter [29]. Cellular, molecular, and biochemical changes underlying cerebral small vessel damage can easily be assessed using animal models of these rare single-gene disorders. Unraveling the genetic aspect of cSVD could lead to an improved understanding of pathogenesis of cSVD, diagnosis and treatment. Table 2 is presenting the summary of various genetic determinant of the cSVD along with some of its uniform descriptors [30-35].
Traditional risk factors such as hypertension or diabetes mellitus play their important role in development of cSVD, but the exact pathogenesis of cSVD is still unclear [36]. Increased permeability of the BBB and endothelial dysfunction has been found to be associated with cSVD in several lines of evidence. BBB disruption is important pathological features of cSVD. Thus, circulating biologic markers of endothelial dysfunction might play a crucial role in identification of cSVD [37,38].
The BBB is a specialized physical and functional barrier that protects the brain from both invading pathogens and circulating immune cells that may enter and cause damage. It is comprised of endothelial cells (ECs) with tight junctions between them. Tight junctions act as a primary defense of the BBB and prevent cells and molecules from passively crossing into the brain [39]. Damage to BBB thus allows the entry of pathogens or immune cells and disturbs the function of the brain [40].
A widely accepted hypothesis is that with increasing age and the presence of chronic hypertension, there is a loss of the ability to self-regulate cerebral blood flow in response to variations in blood pressure, this, together with higher arterial stiffness, produces an increased speed and pulsatility of flow in the cerebral arterioles. These hemodynamic changes would lead to damage in the cerebral endothelium of the BBB and an alteration of its permeability through an increase of the shear stress [41].
BBB leakage has been shown to be a common feature of cSVD supported by the accumulating lines of evidence (Table 3) [37,41-45]; therefore, endothelial dysfunction seems to be a pivotal factor contributing to the pathogenesis of cSVD [8]. Levels of circulating biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction have been found to be elevated in the blood corresponding to cSVD patients [38]. Although the role of other components of the BBB, including pericytes [46] and oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs), has also been suggested in stabilization of BBB and these components are considered potential contributor to the microvascular damage in cSVD along with endothelium [47]. The fact of the matter is that various components of BBB interact with each other which play the pivotal role in the discovery and development of new therapies.
Endothelial dysfunction has been found to lead to cSVD by various mechanisms. One of the hypotheses suggests the reduction in cerebral flow (hypoperfusion) in cSVD patients [48]. Cerebral flow is regulated by nitric oxide signaling which has been identified as a marker for endothelial dysfunction [49]. In another study, endothelial failure and BBB integrity was found to be associated with severity of WMH and there was significant decrease in integrity of ECs in WMH compared with normal white matter [50]. Another line of evidence suggests the increased BBB permeability due to endothelial dysfunction subsequently leads to brain parenchyma lesion. Support in this argument has been documented with higher cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)/serum albumin (SA) ratio (marker of BBB disruption) in dementia and patients with leukoaraiosis [37]. Figure 1 depicts the alteration in BBB and endothelial dysfunction in cSVD. Figure 2 shows the molecular mechanism of several hereditary forms of cSVD.
Evidence of endothelial failure in cSVD has begun to emerge in the form of elevated levels of markers for endothelial dysfunction in the blood of cSVD patients. In many of the studies, although circulating biomarkers were evaluated individually relying on single pathway, conceptually, different pathways should be taken in to the consideration to study several biomarkers simultaneously.
Inflammation markers: Higher expression of endothelial markers such as intracellular adhesion molecule 1, was proved to be associated with WMH progression, and supported the role of endothelial dysfunction in cSVD [51]. In many population-based cohorts, association between inflammatory markers and cSVD has also been reported. C-reactive protein is one abundantly studied marker in this line [52-54]. An independent association was reported with both lacunar infarcts and WMH in all the studies in which asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) levels were measured [55,56]. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 has association with WMH [57]. Besides this, several other inflammatory endothelial biomarkers and their association with WMH and/or lacunar infarcts were also studied by many research groups. Some of these include E-selectine, neopterin, and vascular cell adhesion molecule [58]. Moreover, consistent association of ADMA [59] and circulating progenitor cell were suggested in CADASIL patients [60].
Hyperhomocysteinemia: In several population-based studies, increased level of homocysteine (HCY) and WMH were independently associated with silent lacunar infarcts [61-63].
Coagulation markers: Fibrinogen, a large plasma glycoprotein is synthesized in the liver [64]. Fibrinogen and its breakdown products are cleared from brain tissue by a local tissue plasminogen activator/plasminogen system [55]. Fibrinogen was assumed to be a faithful marker of BBB dysfunction for several reasons [65]. Interestingly, elevated levels of tissue factor pathway inhibitor, was found in lacunar infarct patients [66]. In a small study of Kario et al. [67] 2001, thrombin-antithrombin values were associated with the presence of WMH.
Serum albumin and albuminuria: During BBB dysfunction, albumin extravasations are prevalent in the aging brain and reflect BBB leakage. It is found to be associated with severe white matter lesions in cSVD [68]. Increased CSF/SA ratio, a marker of BBB breakdown, has also been reported in vascular dementia [69] and in patients with white matter changes on neuroimaging [70].
Albuminuria, an early marker of kidney disease [71] has also been proposed as a sensitive biomarker of systemic endothelial dysfunction [72]. There is documentation of an association between albuminuria and SVD neuroimaging markers. Many evidences suggest that peripheral systemic microvascular disease biomarkers could be useful in the evaluation of brain microvascular damage [73].
Serum neurofilament: Neurofilament (NfL) is an essential scaffolding protein of the neuronal cytoskeleton. On axonal damage, NfL is released into the extracellular space and subsequently into the CSF and blood and thus measuring NfL levels is a more direct approach to represent neuronal damage [5]. More recently, serum NfL is found to be increased in patients with a recent small subcortical infarct (RSSI). This has suggested NfL as a blood biomarker for active cSVD [74].
Abnormal endothelial functioning alone is not responsible in development of cSVD pathology. For the maintenance of BBB, other cellular components such as pericytes, astrocytes, and OPCs, are also thought to be essential although their exact contribution is yet to known. In fact, the impact of disrupted cross talk among BBB cell components in this regard is of great significant in understanding molecular mechanism and early phase identification of disease [75]. Interestingly, the role of pericytes in cSVD has been reported in CADASIL studies where genetic determinant of CADASIL (NOTCH3 gene), was shown to be expressed in pericyte that consequently contributed to pathogenesis by the abnormal interactions between pericytes and EC [48].
Changes to oligodendrocytes results in the loss of white matter integrity, which is an important aspect of cSVD. There are also many evidences that provide data of EC-oligodendrocyte signaling in cSVD. In general, endothelium secretes the factors responsible for survival and growth of OPC. Endothelial dysfunction in cSVD patients alters the secretion of releasing factors from ECs, which eventually affect oligodendrocyte survival and make them prone to damage [76]. One hypothesis suggests that signaling between dysfunctional ECs and oligodendrocytes may alter their ability to cope up to the damage caused by hypoperfusion in human with cSVD. Another hypothesis relies on the fact that angiogenesis in cSVD may impair migration of OPC upon blood vessels and thus reduce the repair process [47].
Cerebrovascular diseases and stroke are usually kept under large and small vessel domains and different types of pathologies thereof. However, their pathology affects each other in some or other way. It is supposed that large and small artery cross talk is responsible for causing cerebrovascular diseases [77] but whether large artery pathology alter small arteries or viceversa, is a question yet to be addressed. Even, spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR) are being used both as a established model of small vessel arteriopathy and a large artery disease [78].
Many of recent studies established a fact that pathological mechanism of large vessel disease and SVD are distinct with each other [36]. Nevertheless, both processes may have their cooccurrence and could be overlapping. Interestingly, both subtypes of vascular disease share the similar risk factors such as aging and hypertension [79]. In many instances, increased large artery stiffness transmits the excessive flow pulsatility into the cerebral microcirculation as well as causing diastolic hypoperfusion which both damage microvascular wall thus leading to arteriolosclerosis and white matter damage [80-82]. Therefore, it would not be incorrect to say that both small and large artery disease make a continuum and interact dynamically. This hypothesis has been proved in several studies with animal models that have demonstrated disruption of the endothelial tight junction [83] and increase of white matter disease [84] in animal models with bilateral common carotid artery (CCA) stenosis. Moreover, arterial stiffness in carotid and femoral arteries has been associated with the presence of cSVD markers [85]. The same results along the line have shown decreased arterial elasticity of the CCA in cSVD patients when compared with normal individuals [86].
Neuroimaging plays a central role in the diagnosis and characterization of cSVD since parenchymal lesions caused by small vessel changes have been adopted as markers of cSVD [4]. Manifestation from neuroimaging has a wide spectrum ranging from RSSIs that can present with stroke to relatively more insidious clinically silent lesions. The silent lesions include WMH in the periventricular and deep white and grey matter, enlarged PVSs, lacunes, CMBs, and cerebral atrophy [87]. However, the definitions and terms of these lesions have varied significantly among studies. Therefore, an expert group in cSVD, Wardlaw et al. [88] proposed definitions and terminology for the structural neuroimaging features of cSVD to avoid confusion and improve clarity on cSVD in publication which is popularly referred as STandards for ReportIng Vascular changes on nEuroimaging (STRIVE). Neuroimaging features of SVD have been previously reviewed in depth [89]. Table 4 shows the details of each biomarker with their definitions and disease specific aspects. The cumulative effects of cSVD lesions can best determine the clinical impact and severity of the disease, rather than the individual lesions themselves [90].
cSVD can be visualized routinely on computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain. However, advanced imaging methods, including fluid-attenuated inversion recovery, T2-weighted, T1-weighted and gradient echo/T2*/susceptibility-weighted sequences and diffusion tensor imaging can provide a full spectrum of cSVD and thus will help in early detection of disease [91]. Figure 3 depicts the imaging of all four characteristic features of cSVD. Advances in imaging techniques have provided new insights into mechanisms of cSVD which consequently enables us to explore prevention and treatment strategy towards cSVD. Amyloid PET, widely being used in diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), also has provided proof-of-concept data on CAA and its various manifestations [92]. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI has also been applied to measure permeability of BBB in cSVD patients [41]. It could also be used to elaborate permeability maps showing white matter permeability and could become an advanced diagnostic tool in cSVD diagnosis.
Recently, a ‘total SVD score’ term has been proposed which composite four established imaging biomarkers of cSVD (WMH, lacunes, PVS, and CMB) and estimate the overall burden of cSVD. A total SVD burden score is a better representation of the overall effect of cSVD on the brain rather than taking only one or two individual features separately on consideration. Total SVD burden is visually rated on a scale of 0 to 4. In this score, a point is allocated to each of the following: presence of lacunes, presence of CMB, moderate to severe PVS, and moderate to severe periventricular/deep WMH [90,93]. The total SVD score reflects overall burden of all markers and stratifies the severity of cSVD in a simple and pragmatic way. It may have potential of assessment of risk factors and interventions to prevent cSVD progression.
In medical imaging, image acquisition and image interpretation have both impacts upon accurate assessment of disease. Mostly, medical image interpretations require human observer, but interpretation by humans is limited due to large biasness and variations across interpreters, its subjectivity and human error [94]. Since medical imaging plays a prominent role in the diagnosis of cSVD, interests in application of computerized tools, specifically neural networking, machine learning, and deep learning in image processing have increased significantly for correct delineation of severity of cSVD.
Neural networks are a type of learning algorithm which comprises of neurons or units with some activation a and parameters; W, B, where W is a set of weights and B a set of biases [95]. Neural network is dominated in the field of health care because it has ability to capture the behavior of disease and to predict disease severity and its classification. Processes in neural networking comprised of medical image pre-processing, segmentation, object detection and recognition [96].
Machine learning is often recognized as a subdiscipline of neural networking. Concepts of machine learning have been applied to medical imaging for decades, most notably in the areas of computer-aided diagnosis, content-based image retrieval, automated assessment of image quality and functional brain mapping. Machine learning analyses are a data-driven approach, where algorithm works with a large number of possible predictor variables. In this supervised learning, the predictive model represents the assumed relationship between input variables in x and output variable y. The application of machine learning allows analytical flexibility in selecting the predictor variables, the settings of the machine learning analysis, and the clinical endpoint. To define endpoints apriori, pre-registration of analysis parameters could be carried out [97]. More recently, machine learning paradigm has been used for stroke risk stratification using ultrasonic echolucent carotid wall plaque morphology [98]. In another similar study, stroke risk stratification based on plaque tissue morphology using carotid ultrasound was improved in their performance by embedding pollingbased principal component analysis strategy into the machine learning framework to select and retain dominant features, resulting in superior performance [99]. Machine learning analyses compute and distinguish one feature from other by trained dataset. However, when several features are taken into consideration, it may give biased results. Table 5 dictating existing applications of machine learning in risk stratification of various diseases along with cSVD [100-112].
Deep learning is an improvement of artificial neural networks, and emerging as a promising machine learning tool in the medical imaging and domains of computer vision. It consists of more layers that permit higher levels of abstraction and improved predictions from data [113]. More specifically, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) have been recognized as a leading tool among groups of medical image analysis. CNN and other deep learning processes are giving outstanding results in applications of image analysis, interpretation, and risk stratification in current scenario. Nevertheless, CNN were applied as long ago as 1996 in medical image processing to the identification of biopsy-proven masses and normal tissues from mammograms [114]. Application of deep CNN in correct identification of cSVD markers and stratification in cSVD in to low, medium, and high severity is also well known undoubtedly. More recently, deep three-dimensional CNN were shown for automated detection of lacunes of presumed vascular origin. As the location information is important for the analysis of lacunes, network was equipped with contextual information using multiscale analysis and integration of explicit location features. Further, networks were trained, validated, and tested on a large dataset of 1,075 cases [115]. In another work, location sensitive deep CNN was proposed for segmentation of WMHs in MRI on large datasets. For this, network was integrated with the anatomical location information and shown to outperform a conventional segmentation method with both hand-crafted features and CNNs not integrated with location information [116].
The typical CNN architecture for image processing consists of a series of layers of convolution filters, interspersed with a series of data reduction or pooling layers. Figure 4 illustrates typical CNN architecture. The convolutional layers act as feature extractors, and thus they are learnt the feature representations of their input images. The neurons in the convolutional layers are arranged into feature maps. Filter bank (set of trainable weights) connects each neuron in a feature map to the neurons in the previous layer [113]. The convolution filters detect increasingly more relevant image features, and then higher order features. Pooling layers reduce the spatial resolution of the feature maps. Several convolutional and pooling layers are usually stacked on top of each other to form a deep model and retrieve more abstract feature representations. The fully connected layers interpret these feature representations and execute the function of high-level reasoning [94]. Deep learning is widely considered as current state-of-the-art leads to enhanced accuracy and took image analysis in cSVD to new horizon with respect to risk assessment, segmentation and stratification of progress of imaging markers and so cSVD.
This section presents special notes on associated diseases of cSVD with cerebral as well as non-cerebral component. Cerebral diseases include AD, Parkinson’s disease (PD) which is found to be closely related to cSVD. Non-cerebral diseases discussed here are subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH), hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, and branch retinal artery occlusion (BRAO) which have direct or indirect association in pathology and occurrence of cSVD.
There is much evidence suggesting the contribution of cSVD to the occurrence of AD. It has been well identified that there is an association of AD and key imaging markers of cSVD such as lacunar infarct, WMH, and CMBs [117]. Several studies showed the relationship between lacunar infarct, and components of Alzheimer’s pathology including amyloid β (Aβ) and tau pathology. Kandimalla et al. [118] implicates the association of higher Aβ42 and lower tau in AD. Lacunar infarctions could be tightly linked to higher levels of plasma Aβ40 and plasma Aβ40 in the AD patients [119]. Furthermore, CMBs in AD have been shown more closely coupled with CAA [120]. CMBs were also responsible for the alterations of Aβ metabolism in AD [121]. In another study, patients with early AD were detected by multiple CMBs in 7 T MRI tests [122]. It is also well established that WMH and cerebral atrophy are significant manifestations of AD [123] and also an imaging determinant of cSVD [124]. Another common clinical characteristic is cognitive decline and dementia, which is found in both AD and cSVD [125]. However, it remains unclear by what mechanism cSVD and AD pathology and their association impacts the cognitive decline and dementia. Evidence in this line came from the work of Kester et al. [126] who examined the deposition of amyloid in cSVD patients and revealed that levels were aggravated, especially APOE ε4 carriers, suggesting pathophysiological synergy between AD and cSVD. More recently, cSVD burden was found to be associated with selective disruption of cortical hub grey matter network integrity in AD brains [127]. It is suggested that treatment and prevention for cSVD can be beneficial for AD. Statins have been assumed to have role in treatment of neurodegeneration due to AD since it is beneficial in cSVD [117]. Cilostazol, a type-III phosphodiesterase inhibitor, has been shown to prevent white matter vacuolation and rarefaction induced by bilateral CCA occlusion in rats. Treatment of cilostazol has been demonstrated to improve BBB permeability and reduced gait disturbance, and visual impairment. When applied as an add-on therapy in AD patients, it is found to reduce the decline of cognitive function in those patients [128].
PD is the second most common neurodegenerative disease in the elderly. Recently, PD was evaluated as an important risk factor in the prevalence of ischemic stroke [129]. Additionally previous studies also suggested relationship between cSVD and mild parkinsonian sign (MPS), which are known as subtle motor disturbances. SVD may result in MPS by interfering with basal ganglia-thalamocortical circuits involving both the frontal and parietal lobes. Severe white matter lesions and the presence of lacunar infarcts were independently associated with the presence of MPS [130]. Therefore, cSVD imaging markers could be very useful in early detection of patients with motor impairment.
cSVD at baseline, has role in the etiology of parkinsonism. High WMH volume and a high number of lacunes was found to be directly associated with incident parkinsonism [131]. In this context, Hatate et al. [132] concluded that total SVD score might be helpful marker for MPS, especially deep CMB are of particular interest. In addition, cSVD cases had more frequent biomarker of neurologic diseases, such as brain stem raphe hypoechogenicity, substantia nigra hyperechogenicity and enlarged third ventricles. Substantia nigra hyperechogenicity was linked with gait disturbances, extrapyramidal features, and cognitive impairment. Brain stem raphe hypoechogenicity was correlated with the depression [133].
Individual cSVD markers and total SVD score has been investigated in many cross-sectional [134,135] and longitudinal research studies [136]. The conclusion has been a significant association with lower/impaired cognitive function. New evidence in this line was reported recently in a longitudinal study which found significant cognitive decline particularly in executive function in concert with higher total cSVD score in patients with hypertension [5]. Earlier to this, an association of composite cSVD score was demonstrated with lower global cognitive function in particular impairment of executive function, language, and visuoconstruction [137]. Impact of cSVD on cognition depends on lesion location. Many case studies have suggested that small infarcts in the internal capsule, thalamus and caudate nuclei leads to marked cognitive impairment. Emerging evidence in the field is in the form of lesion-symptom mapping studies, which provided additional information on the impact of lesion location on the different domains of cognitive functioning [138].
Cognitive impairment in the elderly is often a mixed pathology (AD and cerebral microangiopathy) which may increase the risk of dementia [139]. CMB were reported to be an independent factor to heighten the risk of dementia [140]. Clasmatodendrosis along with WMHs and frontal white matter changes, is another contributing factor in cSVD dementia [141]. It is also observed that high levels of total HCY do well to predict the incident and risk factors of dementia. Thus, it could be an effective target in the prevention of dementia [142].
Depressive symptoms are also a major clinical manifestation of cSVD. However, they are largely poorly investigated [143]. WMH, lacunar infarcts, and CMB were associated with more severe depressive symptoms [144]. In another finding, loss in white matter integrity was directly related to depressive symptoms in cSVD patients [145].
The connection between cSVD and epilepsy has been under-researched. Some reports suggest that cSVD and hypertension may implicit the risk of epilepsy [146,147]. Experimental studies on SHRs (the model of cSVD) suggested predisposal of cSVD to temporal lobe epilepsy more than any other type of epilepsy [148].
Gait and balance impairment highly prevails in the elderly, which increases the risk of falls, institutionalization, and mortality. Gait disorder is considered the second most common consequence of cSVD after cognitive impairment [149]. Gait disturbances followed by incontinence and dementia were considered as clinical symptoms of normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH), a disorder found mainly in the elderly with age above 60 years. More interestingly, PD, AD, and vascular dementia have high comorbidity with NPH [150]. In a recent study, the most frequent initial symptoms of NPH were determined which was gait impairment and cognitive decline in men and women, respectively, and the most frequent comorbidities were hypertension and diabetes in men and women, respectively [151].
Most investigations relied only on a single imaging marker of the cSVD and its association with gait and balance disturbance [152,153]. More recently, the impact of individual cSVD markers and global SVD score together has been investigated in gait speed. Among cSVD markers WMH was the significant driving force on a patient’s performance in the gait impairment.
Some clinical disorders, which do not have any direct connection with brain, have been found to be associated with vascular resistance, arterial wall stiffening and endothelial dysfunction, which in turn render them for possessing a potential relationship with cSVD.
SCH has been related with atherosclerosis and elevated risk of ischemic stroke. Zhang et al. [154] elucidated the association of SCH with the presence of WMH, CMB, and composite cSVD burden in patients with transient ischemic stroke. In another report, correlation of arteriolar wall thickness was studied with many factors including HCV and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and concluded that HCV, not HIV establishes an independent risk factor to cerebrovascular pathology [155]. However, some previous studies suggested the increased risk of ischemic stroke in HIV infected patients [156,157]. Patients receiving high active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), in particular, suffered with injury to their vessel walls or metabolic abnormalities that eventually provoked the development of atherosclerotic large vessel disease and myocardial infarction [158]. Furthermore, the potential impact of HAART on small vessel results in cognitive impairment and abnormal metabolism in HIV-infected adults [159]. Another earlier finding suggested that WMHs are associated with HIV seropositive individuals [160]. Recently, during investigation of the BRAO, it was suggested that small vessel etiology may play a pivotal role in pathophysiology of BRAO [161]. The above investigations give another dimension of cSVD research and exploration in the direction of linkage to several other non-cerebral disorders.
Advancement in the elucidation of the disease mechanism will allow us to increase the understanding of the disease pathways, pathophysiology, and common denominator of cSVD which will be the key for innovation in molecular target therapy. BBB rescuing could shed light on other treatment options. MRI markers for cSVD and assessment of global burden by total SVD score provide risk stratification for cSVD in clinical settings and play a crucial role in clinical research. Advancement in image classification processes by embellishing it with stateof-the-art tools of deep learning and big data has enabled correct delineation of the disease and accurate assessment of severity of cSVD.
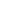
Figure 1.
Alteration in blood-brain barrier (BBB) and endothelial dysfunction in cerebral small vessel disease. (A) Schematic representation of the BBB in normal condition (healthy individual), which consists of the monolayer of endothelial cell, connected by tight junctions and resting on the basal lamina. Circulating blood cells, such as neutrophils and monocytes, are also part of the unit, given the close interaction with the luminal surface of endothelial cells and their role in immune surveillance. Tight junctions consist of three main groups of proteins. They are transmembrane proteins (claudins, occludin, cadherins) and accessory proteins. These proteins interact to form a barrier from which minimal passive extravasation of plasma proteins, inorganic solutes or even water molecules occur. (B) Disassembly of proteins forming tight junction causes disruption of tight junctions leading to increased BBB permeability to small and large macromolecules. (C) Progressive BBB damage and leakiness results in stiffening of the vessel wall due to degradation of basement membrane (BM) and accumulation of extracellular matrix component. Leakiness in BBB also leads to immune cell infilteration and inflammation. TJ, tight junction; AJ, adherence junction; ZO, zonula occludens; MM-9, matrix metalloproteinases-9.
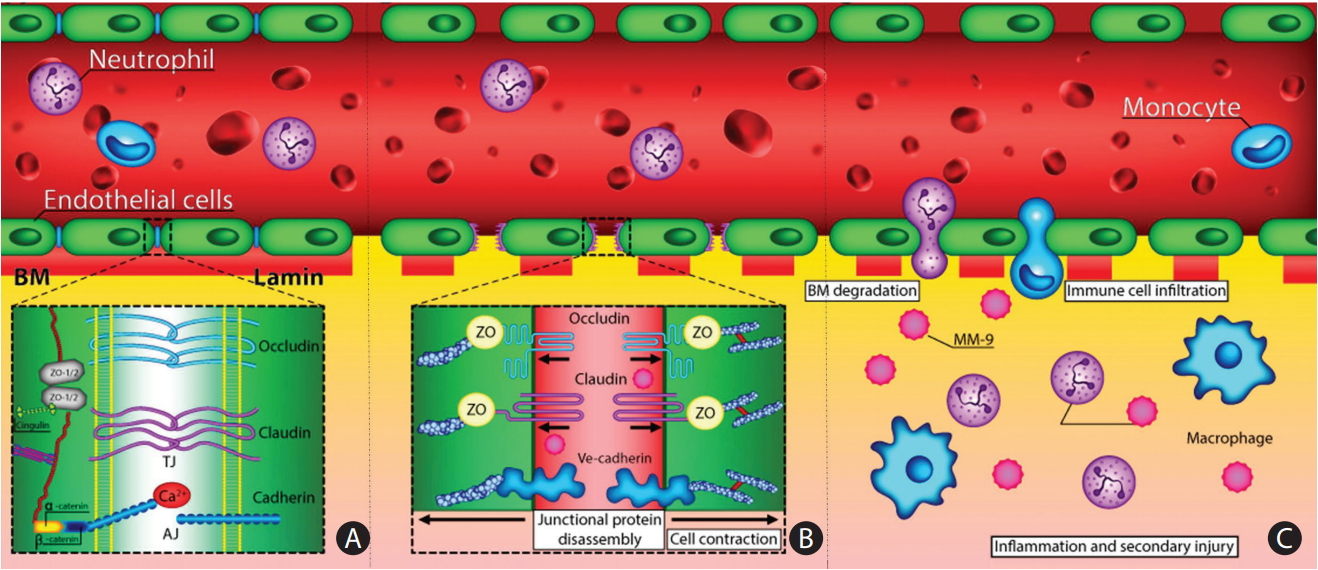
Figure 2.
Molecular mechanism of several hereditary forms of cerebral small vessel disease namely cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL), cerebral autosomal recessive arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CARASIL), and incontinentia pigmenti and their pathophysiology in small vessel causing a disturbed blood-brain barrier (image courtesy: AtheroPoint™, Atheropoint, Roseville, CA, USA). SMAD, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog; NEMO, nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) essential modulator; IKK, IκB kinase; TAK, TGF-β-activated kinase; TAB, TGF-β activated kinase 1 (MAP3K7) binding protein; TNFR, tumor necrosis factor receptor; GOM, granular osmophilic material; TGF-βR, transforming growth factor β receptor; ECM, extracellular matrix; LTBP-1, latent transforming growth factor β binding protein 1; LAP, latency-associated protein; HTRA1, high-temperature requirement a serine peptidase 1; N3ECD, extracellular domain of NOTCH3.

Figure 3.
Neuroimaging markers of cerebral small vessel disease. (A) Recent small subcortical infarct on diffusion weighted imaging (arrow). (B) Lacune on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery imaging (FLAIR) (arrow). (C) White matter hyperintensity on FLAIR imaging (arrows). (D) Perivascular spaces on T1-weighted imaging (arrows). (E) Deep microbleeds on gradient recalled echo (GRE) T2 weighted imaging (arrows). (F) Lobar cerebral microbleeds on GRE imaging (arrows).

Figure 4.
Architecture of typical Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) for image processing. The typical CNN architecture for image processing consists of a series of layers of convolution filters, interspersed with a series of data reduction or pooling layers. Several convolutional and pooling layers are usually stacked on top of each other to form a deep model and retrieve more abstract feature representations. The fully connected layers interpret these feature representations and execute the function of high-level reasoning.
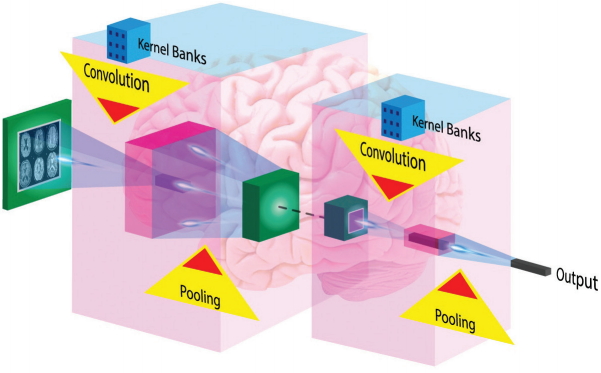
Table 1.
Clinical and neuroimging characteristic difference in the two subtypes of cSVD-amyloidal and non-amyloida [15]
Table 2.
Cerebral small vessel disease subtype based on genetic variation using uniform descriptors
| Type of disease (incidence) | Age at presentation | Presence of accumulated material | Vessels involved | Presence of other location possible | Known genetic alteration | Consequences due to genetic alteration | Possibly involved comorbidities (hypertension, diabetes) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) | Adults | Granular osmiophilic material | Plasma membrane of vascular muscle (smooth muscle cell) | - | Missense mutation in the N3ECD | Alters the number of cysteine residues in the N3ECD, leading to accumulation and deposition of Notch3ECD | Ischemic attacks or strokes, migraine with aura, psychiatric manifestations such as depression and apathy, and impaired memory | Joutel et al. (1996) [30] |
| Cerebral autosomal recessive arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CARASIL) | Adults | Deposition of hyaline material in the wall | Splitting of the internal elastic membrane | - | Homozygous mutations in HTRA1 gene | Interferes the enzymatic property of the protease | Early-onset lacunar stroke, progressive memory dysfunction, gait disturbance, and low back pain | Tikka et al. (2014) [31] |
| Incontinentia pigmenti | Infant | None | Loss of brain endothelial cells (string vessel) | Skin and eyes | Mutations in the NEMO gene | Inactivate NEMO which is an essential subunit of the IκB kinase complex | Neurological symptoms may precede or follow skin lesions | Iejima et al. (2015) [32] |
| Collagen IV related cSVD | Adults | - | Impaired synthesis of the basement membrane and blood vessel fragility | - | Mutations in COL4A1 and COL4A2 genes | Impairing in the formation of the resulting collagen molecule | HANAC syndrome | Gould et al. (2006) [33] |
| Retinal vasculopathy with cerebral leukodystrophy | Adults | Accumulation of genetic material in the cells | Vessel wall degeneration | - | Frameshift mutations in TREX1 which encodes a 3’-5’ exonuclease | Impairment of this enzyme trigger immune system reactions | Vision loss, lacunar strokes and ultimately dementia, HERNS | Kolar et al. (2014) [34] |
| Fabry disease | More than 55 years of age | Accumulation of glycolipids | Walls of small blood vessels, nerves, glomerular and tubular epithelial cells, and cardiomyocytes | - | Mutation in lysosomal GLA gene | Absent or deficient lysosomal GLA activity | Various stroke mechanisms | Hsu et al. (2017) [35] |
N3ECD, extracellular domain of NOTCH3; HTRA1, high-temperature requirement a serine peptidase 1; NEMO, nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) essential modulator; cSVD, cerebral small vessel disease; COL4A1, collagen type IV alpha 1 chain; COL4A2, collagen type IV alpha 2 chain; HANAC, hereditary angiopathy with nephropathy, aneurysms, and muscle cramps; TREX1, three prime repair exonuclease 1; HERNS, hereditary endotheliopathy with retinopathy, nephropathy, and stroke; GLA, α-galactosidase A.
Table 3.
Studies investigating the association of blood-brain barrier permeability and cerebral small vessel disease
| Summary of evidence | MRI marker | Disease phenotype | Study population | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in terms of leakage of plasma components into the vessel wall and surrounding brain tissue leading to neuronal damage, which contribute in development of lacunar stroke, leukoaraiosis, and dementia | Leukoaraiosis | Dementia | Review | Wardlaw et al. (2003) [37] |
| Lacunes | Lacunar stroke | |||
| Comparison of subtle generalized BBB leakiness in patients with lacunar stroke and control patients with cortical ischemic stroke. Patients with lacunar stroke have subtle, diffuse BBB dysfunction in white matter. | Lacunar stroke | - | 51 Lacunar and 46 cortical stroke patients | Wardlaw et al. (2009) [42] |
| Increased BBB permeability in cSVD, and this is particularly seen in cSVD with leucoaraiosis. | Leukoaraiosis | - | 15 Controls and 24 cSVD patients group | Topakian et al. (2010) [43] |
| Patients with Binswanger’s disease (a progressive disease of cSVD) have a persistent failure of the BBB that fluctuates between white matter regions over time. They also found association of BBB disruption with the development of WMHs. | WMH | Binswanger’s disease | 22 Subjects with clinical features of BD and 16-age matched control | Huisa et al. (2015) [44] |
| Lacunes | ||||
| Larger tissue volume with subtle BBB leakage and more extensive leakage in patients with cSVD than in controls | WMH | - | 80 Patients with cSVD and 40 age- and sex-matched controls | Zhang et al. (2017) [41] |
| CGH | ||||
| Association of BBB leakage with development of cSVD-asso-ciated brain damage. BBB leakage was high in normal-appearing white matter with WMH and causative factor for worsening cognition. | WMH | Dementia | 264 Patients (63 patients without BBB imaging had slightly more severe strokes than the 201 with BBB imaging) | Wardlaw et al. (2017) [45] |
| Lacunar or mild cortical ischemic stroke |
Table 4.
Terms, definitions, and disease specific aspect for key neuroimaging markers of cerebral small vessel disease [88]
Table 5.
Application of machine learning programmes in risk segmentation of various diseases
| Serial no. | Disease | Method used/developed | Diagnostic accuracy | Risk assessment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | cSVD | Novel combined automated white matter lesion segmentation algorithm and lesion repair step additionally GPR was used to assess if the severity of SVD | Family wise error corrected P<0.05 | The volume of white matter affected by WMH was calculated, and used as a covariate of interest in a voxel-based morphometry and voxel-based cortical thickness analysis. | Lambert et al. (2015) [100] |
| 2 | cSVD | Trained SVMs with polynomial as well as radial basis function kernels using different DTI-derived features while simultaneously optimizing parameters in leave-one-out nested cross validation | 77.5%-80.0% | To distinguish a MCI performance with high sensitivity which is a common condition in patients with diffuse hyperintensities of cerebral white matter | Ciulli et al. (2016) [101] |
| 3 | cSVD | SVM to classify the burden of PVS in the basal ganglia region | 81.16% | To assess PVS burden from brain MRI. As enlarged PVSs relate to cerebral SVD. | Gonzalez-Castro et al. (2017) [102] |
| 4 | Psoriasis lesions | Psoriasis risk assessment system | 99.84% | Risk assessment to classify disease into five levels of severity: healthy, mild, moderate, severe and very severe | Shrivastava et al. (2017) [103] |
| 5 | Fatty liver disease | Extreme learning machine-based tissue characterization system | 96.75% | Risk stratification of ultrasound liver images | Kuppili et al. (2017) [104] |
| 6 | Lung disease | Two stage CADx cascaded system | 99.53% | Lung disease risk stratification | Than et al. (2017) [105] |
| 7 | Kawasaki disease | Random forest classifier | 79.7% | For immunoglobulin resistance in Kawasaki disease. Abnormal liver markers and percentage neutrophils | Takeuchi et al. (2017) [106] |
| 8 | Cardiovascular disease | Artificial neural cell system for classification | - | Risk factors related to diet/lifestyle, pulmonary function, personal/family/medical history, blood data, blood pressure, and electrocardiography | Tay et al. (2015) [107] |
| 9 | Familial breast cancer | Fuzzy cognitive map | 95% | Assessment of personal risk for developing familial breast cancer | Papageorgiou et al. (2015) [108] |
| 10 | Cardiovascular disease | Natural language processing | 87.5% | Risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, obesity and smoking status | Khalifa et al. (2015) [109] |
| 11 | Psychosis proneness | General linear model | Statistically significant accuracy (P=0.017) | Characterising people at clinical and genetic risk of developing psychosis | Modinos et al. (2012) [110] |
| 12 | Diabetes mellitus | Artificial immune recognition system | 62.8% | Predicting pregnant women who have premonition of type 2 diabetes | Lin et al. (2011) [111] |
| 13 | Acute coronary syndrome | Averaged one-dependence estimators algorithm | C-statistic 0.877 | Age, Killip class, systolic blood pressure, heart rate, pre-hospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation, history of heart failure, history of cerebrovascular disease | Kurz et al. (2009) [112] |
cSVD, cerebral small vessel disease; GPR, Gaussian process regression; SVD, small vessel disease; WMH, white matter hyperintensity; SVM, support vector machine; DTI, diffusion tensor imaging; MCI, mild cognitive impairment; PVS, perivascular space; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; CADx, computer-aided diagnosis system.
References
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Stroke facts. https://www.cdc.gov/stroke/facts.htm. 2017. Accessed April 3, 2018.
3. Gomes J, Wachsman AM. Types of stroke. In : Corrigan ML, Escuro AA, Kirby DF, editors. Handbook of Clinical Nutrition and Stroke New York, NY: Springer; 2013. p. 15-32.
4. Pantoni L. Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol 2010;9:689-701.


5. Uiterwijk R, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Huijts M, De Leeuw PW, Kroon AA, Staals J. Total cerebral small vessel disease MRI score is associated with cognitive decline in executive function in patients with hypertension. Front Aging Neurosci 2016;8:301.



6. Taylor WD, Aizenstein HJ, Alexopoulos GS. The vascular depression hypothesis: mechanisms linking vascular disease with depression. Mol Psychiatry 2013;18:963-974.




7. Pinter D, Ritchie SJ, Doubal F, Gattringer T, Morris Z, Bastin ME, et al. Impact of small vessel disease in the brain on gait and balance. Sci Rep 2017;7:41637.




8. Farrall AJ, Wardlaw JM. Blood-brain barrier: ageing and microvascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurobiol Aging 2009;30:337-352.


10. Charidimou A, Pantoni L, Love S. The concept of sporadic cerebral small vessel disease: a road map on key definitions and current concepts. Int J Stroke 2016;11:6-18.


11. Biffi A, Greenberg SM. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: a systematic review. J Clin Neurol 2011;7:1-9.



12. Charidimou A, Gang Q, Werring DJ. Sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy revisited: recent insights into pathophysiology and clinical spectrum. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2012;83:124-137.


14. Love S, Miners S, Palmer J, Chalmers K, Kehoe P. Insights into the pathogenesis and pathogenicity of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2009;14:4778-4792.


15. Charidimou A, Jäger HR. Developing biomarkers for cerebral amyloid angiopathy trials: do potential disease phenotypes hold promise? Lancet Neurol 2014;13:538-540.

16. Kirshner HS, Bradshaw M. The inflammatory form of cerebral amyloid angiopathy or “cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation” (CAARI). Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2015;15:54.


17. Raposo N, Planton M, Péran P, Payoux P, Bonneville F, Lyoubi A, et al. Florbetapir imaging in cerebral amyloid angiopathyrelated hemorrhages. Neurology 2017;89:697-704.


18. Thal DR, Ghebremedhin E, Rüb U, Yamaguchi H, Del Tredici K, Braak H. Two types of sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2002;61:282-293.



19. van Opstal AM, van Rooden S, van Harten T, Ghariq E, Labadie G, Fotiadis P, et al. Cerebrovascular function in presymptomatic and symptomatic individuals with hereditary cerebral amyloid angiopathy: a case-control study. Lancet Neurol 2017;16:115-122.


20. Fotiadis P, van Rooden S, van der Grond J, Schultz A, Martinez-Ramirez S, Auriel E, et al. Cortical atrophy in patients with cerebral amyloid angiopathy: a case-control study. Lancet Neurol 2016;15:811-819.



22. Rosenblum WI. Cerebral hemorrhage produced by ruptured dissecting aneurysm in miliary aneurysm. Ann Neurol 2003;54:376-378.


23. Caplan LR. Lacunar infarction and small vessel disease: pathology and pathophysiology. J Stroke 2015;17:2-6.



24. Szpak GM, Lewandowska E, Wierzba-Bobrowicz T, Bertrand E, Pasennik E, Mendel T, et al. Small cerebral vessel disease in familial amyloid and non-amyloid angiopathies: FAD-PS-1 (P117L) mutation and CADASIL. Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies. Folia Neuropathol 2007;45:192-204. Erratum in: Folia Neuropathol 2008;46:92.

25. Fazekas F, Kleinert R, Offenbacher H, Schmidt R, Kleinert G, Payer F, et al. Pathologic correlates of incidental MRI white matter signal hyperintensities. Neurology 1993;43:1683-1689.


26. van Swieten JC, van den Hout JH, van Ketel BA, Hijdra A, Wokke JH, van Gijn J. Periventricular lesions in the white matter on magnetic resonance imaging in the elderly. A morphometric correlation with arteriolosclerosis and dilated perivascular spaces. Brain 1991;114(Pt 2):761-774.



28. Müller K, Courtois G, Ursini MV, Schwaninger M. New insight Into the pathogenesis of cerebral small-vessel diseases. Stroke 2017;48:520-527.


30. Joutel A, Corpechot C, Ducros A, Vahedi K, Chabriat H, Mouton P, et al. Notch3 mutations in CADASIL, a hereditary adult-onset condition causing stroke and dementia. Nature 1996;383:707-710.



31. Tikka S, Baumann M, Siitonen M, Pasanen P, Pöyhönen M, Myllykangas L, et al. CADASIL and CARASIL. Brain Pathol 2014;24:525-544.



32. Iejima D, Itabashi T, Kawamura Y, Noda T, Yuasa S, Fukuda K, et al. HTRA1 (high temperature requirement A serine peptidase 1) gene is transcriptionally regulated by insertion/deletion nucleotides located at the 3’ end of the ARMS2 (agerelated maculopathy susceptibility 2) gene in patients with age-related macular degeneration. J Biol Chem 2015;290:2784-2797.


33. Gould DB, Phalan FC, van Mil SE, Sundberg JP, Vahedi K, Massin P, et al. Role of COL4A1 in small-vessel disease and hemorrhagic stroke. N Engl J Med 2006;354:1489-1496.


34. Kolar GR, Kothari PH, Khanlou N, Jen JC, Schmidt RE, Vinters HV. Neuropathology and genetics of cerebroretinal vasculopathies. Brain Pathol 2014;24:510-518.



35. Hsu TR, Niu DM. Fabry disease: review and experience during newborn screening. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2018;28:274-281.


36. Wardlaw JM, Smith C, Dichgans M. Mechanisms of sporadic cerebral small vessel disease: insights from neuroimaging. Lancet Neurol 2013;12:483-497.


37. Wardlaw JM, Sandercock PA, Dennis MS, Starr J. Is breakdown of the blood-brain barrier responsible for lacunar stroke, leukoaraiosis, and dementia? Stroke 2003;34:806-812.

38. Poggesi A, Pasi M, Pescini F, Pantoni L, Inzitari D. Circulating biologic markers of endothelial dysfunction in cerebral small vessel disease: a review. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2016;36:72-94.



39. Wolburg H, Lippoldt A. Tight junctions of the blood-brain barrier: development, composition and regulation. Vascul Pharmacol 2002;38:323-337.


40. Hawkins BT, Davis TP. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev 2005;57:173-185.


41. Zhang CE, Wong SM, van de Haar HJ, Staals J, Jansen JF, Jeukens CR, et al. Blood-brain barrier leakage is more widespread in patients with cerebral small vessel disease. Neurology 2017;88:426-432.


42. Wardlaw JM, Doubal F, Armitage P, Chappell F, Carpenter T, Muñoz Maniega S, et al. Lacunar stroke is associated with diffuse blood-brain barrier dysfunction. Ann Neurol 2009;65:194-202.


43. Topakian R, Barrick TR, Howe FA, Markus HS. Blood-brain barrier permeability is increased in normal-appearing white matter in patients with lacunar stroke and leucoaraiosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2010;81:192-197.


44. Huisa BN, Caprihan A, Thompson J, Prestopnik J, Qualls CR, Rosenberg GA. Long-term blood-brain barrier permeability changes in Binswanger disease. Stroke 2015;46:2413-2418.



45. Wardlaw JM, Makin SJ, Valdés Hernández MC, Armitage PA, Heye AK, Chappell FM, et al. Blood-brain barrier failure as a core mechanism in cerebral small vessel disease and dementia: evidence from a cohort study. Alzheimers Dement 2017;13:634-643.

46. Ihara M, Yamamoto Y. Emerging evidence for pathogenesis of sporadic cerebral small vessel disease. Stroke 2016;47:554-560.


47. Rajani RM, Williams A. Endothelial cell-oligodendrocyte interactions in small vessel disease and aging. Clin Sci (Lond) 2017;131:369-379.



48. Armulik A, Abramsson A, Betsholtz C. Endothelial/pericyte interactions. Circ Res 2005;97:512-523.


49. Deplanque D, Lavallee PC, Labreuche J, Gongora-Rivera F, Jaramillo A, Brenner D, et al. Cerebral and extracerebral vasoreactivity in symptomatic lacunar stroke patients: a casecontrol study. Int J Stroke 2013;8:413-421.


50. Young VG, Halliday GM, Kril JJ. Neuropathologic correlates of white matter hyperintensities. Neurology 2008;71:804-811.


51. Markus HS, Hunt B, Palmer K, Enzinger C, Schmidt H, Schmidt R. Markers of endothelial and hemostatic activation and progression of cerebral white matter hyperintensities: longitudinal results of the Austrian Stroke Prevention Study. Stroke 2005;36:1410-1414.


52. van Dijk EJ, Prins ND, Vermeer SE, Vrooman HA, Hofman A, Koudstaal PJ, et al. C-reactive protein and cerebral small-vessel disease: the Rotterdam Scan Study. Circulation 2005;112:900-905.


53. Fornage M, Chiang YA, O’Meara ES, Psaty BM, Reiner AP, Siscovick DS, et al. Biomarkers of inflammation and MRI-defined small vessel disease of the brain: the cardiovascular health study. Stroke 2008;39:1952-1959.



54. Satizabal CL, Zhu YC, Mazoyer B, Dufouil C, Tzourio C. Circulating IL-6 and CRP are associated with MRI findings in the elderly: the 3C-Dijon Study. Neurology 2012;78:720-727.


55. Notsu Y, Nabika T, Bokura H, Suyama Y, Kobayashi S, Yamaguchi S, et al. Evaluation of asymmetric dimethylarginine and homocysteine in microangiopathy-related cerebral damage. Am J Hypertens 2009;22:257-262.



56. Pikula A, Böger RH, Beiser AS, Maas R, DeCarli C, Schwedhelm E, et al. Association of plasma ADMA levels with MRI markers of vascular brain injury: Framingham offspring study. Stroke 2009;40:2959-2964.



57. Kim Y, Kim YK, Kim NK, Kim SH, Kim OJ, Oh SH. Circulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 level is associated with cerebral white matter hyperintensities in non-stroke individuals. Eur Neurol 2014;72:234-240.


58. Rouhl RP, Damoiseaux JG, Lodder J, Theunissen RO, Knottnerus IL, Staals J, et al. Vascular inflammation in cerebral small vessel disease. Neurobiol Aging 2012;33:1800-1806.


59. Rufa A, Blardi P, De Lalla A, Cevenini G, De Stefano N, Zicari E, et al. Plasma levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine in cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarct and leukoencephalopathy. Cerebrovasc Dis 2008;26:636-640.


60. Pescini F, Cesari F, Giusti B, Sarti C, Zicari E, Bianchi S, et al. Bone marrow-derived progenitor cells in cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy. Stroke 2010;41:218-223.


61. Vermeer SE, van Dijk EJ, Koudstaal PJ, Oudkerk M, Hofman A, Clarke R, et al. Homocysteine, silent brain infarcts, and white matter lesions: the Rotterdam Scan Study. Ann Neurol 2002;51:285-289.


62. Kloppenborg RP, Nederkoorn PJ, van der Graaf Y, Geerlings MI. Homocysteine and cerebral small vessel disease in patients with symptomatic atherosclerotic disease. The SMARTMR study. Atherosclerosis 2011;216:461-466.


63. Sachdev P, Parslow R, Salonikas C, Lux O, Wen W, Kumar R, et al. Homocysteine and the brain in midadult life: evidence for an increased risk of leukoaraiosis in men. Arch Neurol 2004;61:1369-1376.


64. Aono Y, Ohkubo T, Kikuya M, Hara A, Kondo T, Obara T, et al. Plasma fibrinogen, ambulatory blood pressure, and silent cerebrovascular lesions: the Ohasama study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2007;27:963-968.


65. Bridges LR, Andoh J, Lawrence AJ, Khoong CHL, Poon W, Esiri MM, et al. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction and cerebral small vessel disease (arteriolosclerosis) in brains of older people. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2014;73:1026-1033.



66. Knottnerus IL, Winckers K, Ten Cate H, Hackeng TM, Lodder J, Rouhl RP, et al. Levels of heparin-releasable TFPI are increased in first-ever lacunar stroke patients. Neurology 2012;78:493-498.


67. Kario K, Matsuo T, Kobayashi H, Hoshide S, Shimada K. Hyperinsulinemia and hemostatic abnormalities are associated with silent lacunar cerebral infarcts in elderly hypertensive subjects. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001;37:871-877.


68. Simpson JE, Fernando MS, Clark L, Ince PG, Matthews F, Forster G, et al. White matter lesions in an unselected cohort of the elderly: astrocytic, microglial and oligodendrocyte precursor cell responses. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2007;33:410-419.


69. Skoog I, Wallin A, Fredman P, Hesse C, Aevarsson O, Karlsson I, et al. A population study on blood-brain barrier function in 85-year-olds: relation to Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Neurology 1998;50:966-971.


70. Pantoni L, Inzitari D, Pracucci G, Lolli F, Giordano G, Bracco L, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid proteins in patients with leucoaraiosis: possible abnormalities in blood-brain barrier function. J Neurol Sci 1993;115:125-131.


71. Vogels SC, Emmelot-Vonk MH, Verhaar HJ, Koek HL. The association of chronic kidney disease with brain lesions on MRI or CT: a systematic review. Maturitas 2012;71:331-336.


72. Stehouwer CD, Smulders YM. Microalbuminuria and risk for cardiovascular disease: analysis of potential mechanisms. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006;17:2106-2111.


73. Georgakis MK, Chatzopoulou D, Tsivgoulis G, Petridou ET. Albuminuria and cerebral small vessel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc 2018;66:509-517.


74. Gattringer T, Pinter D, Enzinger C, Seifert-Held T, Kneihsl M, Fandler S, et al. Serum neurofilament light is sensitive to active cerebral small vessel disease. Neurology 2017;89:2108-2114.



75. Rannikmäe K, Davies G, Thomson PA, Bevan S, Devan WJ, Falcone GJ, et al. Common variation in COL4A1/COL4A2 is associated with sporadic cerebral small vessel disease. Neurology 2015;84:918-926.



76. Rajashekhar G, Willuweit A, Patterson CE, Sun P, Hilbig A, Breier G, et al. Continuous endothelial cell activation increases angiogenesis: evidence for the direct role of endothelium linking angiogenesis and inflammation. J Vasc Res 2006;43:193-204.


77. Laurent S, Briet M, Boutouyrie P. Large and small artery crosstalk and recent morbidity-mortality trials in hypertension. Hypertension 2009;54:388-392.


78. Bailey EL, Smith C, Sudlow CL, Wardlaw JM. Is the spontaneously hypertensive stroke prone rat a pertinent model of sub cortical ischemic stroke? A systematic review. Int J Stroke 2011;6:434-444.


79. Khan U, Porteous L, Hassan A, Markus HS. Risk factor profile of cerebral small vessel disease and its subtypes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2007;78:702-706.



80. Boulouis G, Charidimou A, Auriel E, Haley KE, van Etten ES, Fotiadis P, et al. Intracranial atherosclerosis and cerebral small vessel disease in intracerebral hemorrhage patients. J Neurol Sci 2016;369:324-329.


81. Brisset M, Boutouyrie P, Pico F, Zhu Y, Zureik M, Schilling S, et al. Large-vessel correlates of cerebral small-vessel disease. Neurology 2013;80:662-669.



82. Aribisala BS, Morris Z, Eadie E, Thomas A, Gow A, Valdés Hernández MC, et al. Blood pressure, internal carotid artery flow parameters, and age-related white matter hyperintensities. Hypertension 2014;63:1011-1018.



83. Hattori Y, Okamoto Y, Maki T, Yamamoto Y, Oishi N, Yamahara K, et al. Silent information regulator 2 homolog 1 counters cerebral hypoperfusion injury by deacetylating endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Stroke 2014;45:3403-3411.


84. Kitamura A, Saito S, Maki T, Oishi N, Ayaki T, Hattori Y, et al. Gradual cerebral hypoperfusion in spontaneously hypertensive rats induces slowly evolving white matter abnormalities and impairs working memory. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2016;36:1592-1602.


85. Poels MM, Zaccai K, Verwoert GC, Vernooij MW, Hofman A, van der Lugt A, et al. Arterial stiffness and cerebral small vessel disease: the Rotterdam Scan Study. Stroke 2012;43:2637-2642.


86. Huang X, Kang X, Xue J, Kang C, Lv H, Li Z. Evaluation of carotid artery elasticity changes in patients with cerebral small vessel disease. Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8:18825-18830.


87. Vermeer SE, Longstreth WT Jr, Koudstaal PJ. Silent brain infarcts: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol 2007;6:611-619.


88. Wardlaw JM, Smith EE, Biessels GJ, Cordonnier C, Fazekas F, Frayne R, et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol 2013;12:822-838.



89. Norrving B. Evolving concept of small vessel disease through advanced brain imaging. J Stroke 2015;17:94-100.



90. Staals J, Makin SD, Doubal FN, Dennis MS, Wardlaw JM. Stroke subtype, vascular risk factors, and total MRI brain small-vessel disease burden. Neurology 2014;83:1228-1234.



91. Lyoubi-Idrissi AL, Jouvent E, Poupon C, Chabriat H. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging in cerebral small vessel disease. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2017;173:201-210.


92. Farid K, Charidimou A, Baron JC. Amyloid positron emission tomography in sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy: a systematic critical update. Neuroimage Clin 2017;15:247-263.



93. Klarenbeek P, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Rouhl RP, Knottnerus IL, Staals J. Ambulatory blood pressure in patients with lacunar stroke: association with total MRI burden of cerebral small vessel disease. Stroke 2013;44:2995-2999.


94. Rawat W, Wang Z. Deep convolutional neural networks for image classification: a comprehensive review. Neural Comput 2017;29:2352-2449.


95. Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Ghafoorian M, et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal 2017;42:60-88.


96. Shi Z, He L, Suzuki K, Nakamura T, Itoh H. Survey on neural networks used for medical image processing. Int J Comput Sci 2009;3:86-100.


97. Shen D, Wu G, Zhang D, Suzuki K, Wang F, Yan P. Machine learning in medical imaging. Comput Med Imaging Graph 2015;41:1-2.


98. Araki T, Jain PK, Suri HS, Londhe ND, Ikeda N, El-Baz A, et al. Stroke risk stratification and its validation using ultrasonic echolucent carotid wall plaque morphology: a machine learning paradigm. Comput Biol Med 2017;80:77-96.


99. Saba L, Jain PK, Suri HS, Ikeda N, Araki T, Singh BK, et al. Plaque tissue morphology-based stroke risk stratification using carotid ultrasound: a polling-based PCA learning paradigm. J Med Syst 2017;41:98.



100. Lambert C, Sam Narean J, Benjamin P, Zeestraten E, Barrick TR, Markus HS. Characterising the grey matter correlates of leukoaraiosis in cerebral small vessel disease. Neuroimage Clin 2015;9:194-205.



101. Ciulli S, Citi L, Salvadori E, Valenti R, Poggesi A, Inzitari D, et al. Prediction of impaired performance in trail making test in MCI patients with small vessel disease using DTI data. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 2016;20:1026-1033.


102. González-Castro V, Valdés Hernández MDC, Chappell FM, Armitage PA, Makin S, Wardlaw JM. Reliability of an automatic classifier for brain enlarged perivascular spaces burden and comparison with human performance. Clin Sci (Lond) 2017;131:1465-1481.


103. Shrivastava VK, Londhe ND, Sonawane RS, Suri JS. A novel and robust Bayesian approach for segmentation of psoriasis lesions and its risk stratification. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2017;150:9-22.


104. Kuppili V, Biswas M, Sreekumar A, Suri HS, Saba L, Edla DR, et al. Extreme learning machine framework for risk stratification of fatty liver disease using ultrasound tissue characterization. J Med Syst 2017;41:152.


105. Than JCM, Saba L, Noor NM, Rijal OM, Kassim RM, Yunus A, et al. Lung disease stratification using amalgamation of Riesz and Gabor transforms in machine learning framework. Comput Biol Med 2017;89:197-211.


106. Takeuchi M, Inuzuka R, Hayashi T, Shindo T, Hirata Y, Shimizu N, et al. Novel risk assessment tool for immunoglobulin resistance in Kawasaki disease: application using a random forest classifier. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2017;36:821-826.


107. Tay D, Poh CL, Kitney RI. A novel neural-inspired learning algorithm with application to clinical risk prediction. J Biomed Inform 2015;54:305-314.


108. Papageorgiou EI, Jayashree S, Karmegam A, Papandrianos N. A risk management model for familial breast cancer: a new application using Fuzzy Cognitive Map method. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2015;122:123-135.


109. Khalifa A, Meystre S. Adapting existing natural language processing resources for cardiovascular risk factors identification in clinical notes. J Biomed Inform 2015;58 Suppl:S128-S132.


110. Modinos G, Pettersson-Yeo W, Allen P, McGuire PK, Aleman A, Mechelli A. Multivariate pattern classification reveals differential brain activation during emotional processing in individuals with psychosis proneness. Neuroimage 2012;59:3033-3041.


111. Lin HC, Su CT, Wang PC. An application of artificial immune recognition system for prediction of diabetes following gestational diabetes. J Med Syst 2011;35:283-289.


112. Kurz DJ, Bernstein A, Hunt K, Radovanovic D, Erne P, Siudak Z, et al. Simple point-of-care risk stratification in acute coronary syndromes: the AMIS model. Heart 2009;95:662-668.


114. Sahiner B, Chan HP, Petrick N, Wei D, Helvie MA, Adler DD, et al. Classification of mass and normal breast tissue: a convolution neural network classifier with spatial domain and texture images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1996;15:598-610.


115. Ghafoorian M, Karssemeijer N, Heskes T, Bergkamp M, Wissink J, Obels J, et al. Deep multi-scale location-aware 3D convolutional neural networks for automated detection of lacunes of presumed vascular origin. Neuroimage Clin 2017;14:391-399.



116. Ghafoorian M, Karssemeijer N, Heskes T, van Uden IWM, Sanchez CI, Litjens G, et al. Location sensitive deep convolutional neural networks for segmentation of white matter hyperintensities. Sci Rep 2017;7:5110.




117. Cai Z, Wang C, He W, Tu H, Tang Z, Xiao M, et al. Cerebral small vessel disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Interv Aging 2015;10:1695-1704.



118. Kandimalla RJ, Prabhakar S, Binukumar BK, Wani WY, Gupta N, Sharma DR, et al. Apo-E4 allele in conjunction with Abeta42 and tau in CSF: biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 2011;8:187-196.


119. Gurol ME, Irizarry MC, Smith EE, Raju S, Diaz-Arrastia R, Bottiglieri T, et al. Plasma beta-amyloid and white matter lesions in AD, MCI, and cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology 2006;66:23-29.


120. Nakata-Kudo Y, Mizuno T, Yamada K, Shiga K, Yoshikawa K, Mori S, et al. Microbleeds in Alzheimer disease are more related to cerebral amyloid angiopathy than cerebrovascular disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2006;22:8-14.


121. Goos JD, Teunissen CE, Veerhuis R, Verwey NA, Barkhof F, Blankenstein MA, et al. Microbleeds relate to altered amyloid-beta metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 2012;33:1011.e1-1011.e9.


122. Brundel M, Heringa SM, de Bresser J, Koek HL, Zwanenburg JJ, Jaap Kappelle L, et al. High prevalence of cerebral microbleeds at 7Tesla MRI in patients with early Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2012;31:259-263.


123. Guo H, Song X, Vandorpe R, Zhang Y, Chen W, Zhang N, et al. Evaluation of common structural brain changes in aging and Alzheimer disease with the use of an MRI-based brain atrophy and lesion index: a comparison between T1WI and T2WI at 1.5T and 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2014;35:504-512.



124. Aribisala BS, Valdés Hernández MC, Royle NA, Morris Z, Muñoz Maniega S, Bastin ME, et al. Brain atrophy associations with white matter lesions in the ageing brain: the Lothian Birth Cohort 1936. Eur Radiol 2013;23:1084-1092.


125. Kovacic JC, Fuster V. Atherosclerotic risk factors, vascular cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer disease. Mt Sinai J Med 2012;79:664-673.


126. Kester MI, Goos JD, Teunissen CE, Benedictus MR, Bouwman FH, Wattjes MP, et al. Associations between cerebral small-vessel disease and Alzheimer disease pathology as measured by cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers. JAMA Neurol 2014;71:855-862.


127. Nestor SM, Mišić B, Ramirez J, Zhao J, Graham SJ, Verhoeff N, et al. Small vessel disease is linked to disrupted structural network covariance in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 2017;13:749-760.


128. Tai SY, Chen CH, Chien CY, Yang YH. Cilostazol as an add-on therapy for patients with Alzheimer’s disease in Taiwan: a case control study. BMC Neurol 2017;17:40.



129. Song IU, Lee JE, Kwon DY, Park JH, Ma HI. Parkinson’s disease might increase the risk of cerebral ischemic lesions. Int J Med Sci 2017;14:319-322.



130. de Laat KF, van Norden AG, Gons RA, van Uden IW, Zwiers MP, Bloem BR, et al. Cerebral white matter lesions and lacunar infarcts contribute to the presence of mild parkinsonian signs. Stroke 2012;43:2574-2579.


131. van der Holst HM, van Uden IW, Tuladhar AM, de Laat KF, van Norden AG, Norris DG, et al. Cerebral small vessel disease and incident parkinsonism: the RUN DMC study. Neurology 2015;85:1569-1577.



132. Hatate J, Miwa K, Matsumoto M, Sasaki T, Yagita Y, Sakaguchi M, et al. Association between cerebral small vessel diseases and mild parkinsonian signs in the elderly with vascular risk factors. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2016;26:29-34.


133. Pavlović AM, Pekmezović T, Jovanović Z, Medjedović TS, Veselinović N, Norton MC, et al. Transcranial parenchymal sonographic findings in patients with cerebral small vessel disease: a preliminary study. J Ultrasound Med 2015;34:1853-1859.


134. Pantoni L, Poggesi A, Inzitari D. The relation between whitematter lesions and cognition. Curr Opin Neurol 2007;20:390-397.


135. Carey CL, Kramer JH, Josephson SA, Mungas D, Reed BR, Schuff N, et al. Subcortical lacunes are associated with executive dysfunction in cognitively normal elderly. Stroke 2008;39:397-402.


136. Pavlovic AM, Pekmezovic T, Tomic G, Trajkovic JZ, Sternic N. Baseline predictors of cognitive decline in patients with cerebral small vessel disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2014;42 Suppl 3:S37-S43.


137. Xu X, Hilal S, Collinson SL, Chong EJ, Ikram MK, Venketasubramanian N, et al. Association of magnetic resonance imaging markers of cerebrovascular disease burden and cognition. Stroke 2015;46:2808-2814.


138. Biesbroek JM, Weaver NA, Biessels GJ. Lesion location and cognitive impact of cerebral small vessel disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 2017;131:715-728.


139. Gorelick PB, Scuteri A, Black SE, Decarli C, Greenberg SM, Iadecola C, et al. Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia: a statement for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke 2011;42:2672-2713.



140. Miwa K, Tanaka M, Okazaki S, Yagita Y, Sakaguchi M, Mochizuki H, et al. Multiple or mixed cerebral microbleeds and dementia in patients with vascular risk factors. Neurology 2014;83:646-653.


141. Chen A, Akinyemi RO, Hase Y, Firbank MJ, Ndung’u MN, Foster V, et al. Frontal white matter hyperintensities, clasmatodendrosis and gliovascular abnormalities in ageing and poststroke dementia. Brain 2016;139(Pt 1):242-258.



142. Miwa K, Tanaka M, Okazaki S, Yagita Y, Sakaguchi M, Mochizuki H, et al. Increased total homocysteine levels predict the risk of incident dementia independent of cerebral smallvessel diseases and vascular risk factors. J Alzheimers Dis 2016;49:503-513.


143. van Sloten TT, Sigurdsson S, van Buchem MA, Phillips CL, Jonsson PV, Ding J, et al. Cerebral small vessel disease and association with higher incidence of depressive symptoms in a general elderly population: the AGES-Reykjavik study. Am J Psychiatry 2015;172:570-578.



144. Pasi M, Boulouis G, Fotiadis P, Auriel E, Charidimou A, Haley K, et al. Distribution of lacunes in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and hypertensive small vessel disease. Neurology 2017;88:2162-2168.



145. Pasi M, Poggesi A, Salvadori E, Diciotti S, Ciolli L, Del Bene A, et al. White matter microstructural damage and depressive symptoms in patients with mild cognitive impairment and cerebral small vessel disease: the VMCI-Tuscany study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 2016;31:611-618.


146. Maxwell H, Hanby M, Parkes LM, Gibson LM, Coutinho C, Emsley HC. Prevalence and subtypes of radiological cerebrovascular disease in late-onset isolated seizures and epilepsy. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2013;115:591-596.


147. De Reuck J, Nagy E, Van Maele G. Seizures and epilepsy in patients with lacunar strokes. J Neurol Sci 2007;263:75-78.


148. Russo E, Leo A, Scicchitano F, Donato A, Ferlazzo E, Gasparini S, et al. Cerebral small vessel disease predisposes to temporal lobe epilepsy in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Brain Res Bull 2017;130:245-250.


149. van der Holst HM, van Uden IW, Tuladhar AM, de Laat KF, van Norden AG, Norris DG, et al. Factors associated with 8-year mortality in older patients with cerebral small vessel disease: the Radboud University Nijmegen Diffusion Tensor and Magnetic Resonance Cohort (RUN DMC) study. JAMA Neurol 2016;73:402-409.


151. Kuriyama N, Miyajima M, Nakajima M, Kurosawa M, Fukushima W, Watanabe Y, et al. Nationwide hospital-based survey of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus in Japan: epidemiological and clinical characteristics. Brain Behav 2017;7:e00635.



152. Starr JM, Leaper SA, Murray AD, Lemmon HA, Staff RT, Deary IJ, et al. Brain white matter lesions detected by magnetic resonance [correction of resosnance] imaging are associated with balance and gait speed. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2003;74:94-98.



153. de Laat KF, van den Berg HA, van Norden AG, Gons RA, Olde Rikkert MG, de Leeuw FE. Microbleeds are independently related to gait disturbances in elderly individuals with cerebral small vessel disease. Stroke 2011;42:494-497.


154. Zhang X, Xie Y, Ding C, Xiao J, Tang Y, Jiang X, et al. Subclinical hypothyroidism and risk of cerebral small vessel disease: a hospital-based observational study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2017;87:581-586.


155. Morgello S, Murray J, Van Der Elst S, Byrd D. HCV, but not HIV, is a risk factor for cerebral small vessel disease. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 2014;1:e27.



156. Chow FC, Regan S, Feske S, Meigs JB, Grinspoon SK, Triant VA. Comparison of ischemic stroke incidence in HIV-infected and non-HIV-infected patients in a US health care system. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2012;60:351-358.



157. Rasmussen LD, Engsig FN, Christensen H, Gerstoft J, Kronborg G, Pedersen C, et al. Risk of cerebrovascular events in persons with and without HIV: a Danish nationwide population-based cohort study. AIDS 2011;25:1637-1646.


158. Worm SW, Sabin C, Weber R, Reiss P, El-Sadr W, Dabis F, et al. Risk of myocardial infarction in patients with HIV infection exposed to specific individual antiretroviral drugs from the 3 major drug classes: the data collection on adverse events of anti-HIV drugs (D:A:D) study. J Infect Dis 2010;201:318-330.



159. Soontornniyomkij V, Umlauf A, Chung SA, Cochran ML, Soontornniyomkij B, Gouaux B, et al. HIV protease inhibitor exposure predicts cerebral small vessel disease. AIDS 2014;28:1297-1306.