 |
 |
- Search
| J Stroke > Volume 20(2); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Intracranial large artery disease (ILAD) is the major cause of stroke worldwide. With the application of recently introduced diagnostic techniques, the prevalence of non-atherosclerotic ILAD is expected to increase. Herein, we reviewed recent reports and summarized progress in the diagnosis and clinical impact of differentiation between ILAD of atherosclerotic and non-atherosclerotic origin. Our review of the literature suggests that more careful consideration of non-atherosclerotic causes and the application of appropriate diagnostic techniques in patients with ILAD may not only provide better results in the treatment of patients, but it may also lead to more successful clinical trials for the treatment of intracranial atherosclerosis.
Intracranial large artery disease (ILAD) is the major cause of stroke worldwide. There have been significant advances in treatment strategies as a result of a better understanding of the pathophysiologic mechanisms of stroke underlying intracranial atherosclerosis [1-5]. Recently introduced diagnostic techniques, such as vessel wall imaging using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (HR-MRI) and genome-wide association studies (GWASs), enable us to differentiate intracranial atherosclerosis from ILAD of non-atherosclerotic origin. However, the prevalence of ILAD of non-atherosclerotic origin remains unclear. Although non-atherosclerotic ILAD is increasingly diagnosed, many patients with this disease may be misclassified as having intracranial atherosclerosis. We reviewed recent reports and summarized progress in the diagnosis and clinical impact of differentiating between ILAD of atherosclerotic and non-atherosclerotic origin.
We searched PubMed and ClinicalTrials.gov for articles published in English up to August 2017, using the search terms stroke, cerebrovascular disease, and intracranial stenosis. Additionally, we searched references from relevant articles and reviews. The final reference list was generated on the basis of originality and relevance to this topic. We did not discuss individual etiologies of non-atherosclerotic ILAD or imaging techniques in depth, since these topics are reviewed elsewhere [6-9].
Cervicocephalic arterial dissection is a common cause of stroke in young adults and adolescents. Tearing of the vessel wall between the intima and media or adventitia may result in the formation of a thrombus within the lumen, leading to a critical occlusion of the vessel or a thromboembolic episode. Tearing can also cause intracranial bleeding. Intracranial dissection should be suspected in patients with a related clinical syndrome (e.g., sudden neck pain, connective tissue disease, or minor trauma), especially in those who are young and have no atherosclerotic risk factors, or show stenosis at sites of predilection (e.g., the middle cerebral artery segment adjacent to the sphenoid ridge, anterior cerebral artery adjacent to the falx cerebri, or intracranial vertebral artery [VA] near the origin of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery) [9-12].
Cervicocerebral artery dissection accounts for approximately 2% of all ischemic strokes but about 20% of strokes in the young and middle-aged [13]. The prevalence of intracranial dissection among those with ILAD remains unclear and it may be underestimated, since most large studies have examined carotid dissection in non-Asian countries where intracranial dissection is relatively rare, compared with the prevalence in Asia. In addition, spontaneous intracranial dissection may have been misclassified as intracranial atherosclerosis. Pain at the onset of stroke symptoms (a typical clinical feature of dissection), is not commonly reported in most clinical studies, and a history of trauma was more common in patients with extracranial dissection than in those with intracranial dissection [14]. Moreover, luminal imaging, including conventional angiography, may be insufficient for the diagnosis of intracranial dissection if patients do not show aneurysmal dilation.
In non-Asian populations, intracranial dissection is believed to comprise <10% of all spontaneous cervicocephalic artery dissections in adults [15]. However, intracranial dissection is more common than extracranial dissection in Asian populations, in both the anterior and posterior circulation [14,16,17]. Anatomical differences (i.e., intracranial vessel wall thickness and prevalence of arterial hypoplasia) among racial populations may account for the high prevalence of intracranial dissection in Asians. In addition, certain genetic differences may result in variation in the location of arterial diseases among ethnicities (e.g., genetic variation in the elastin gene and the location of the intracranial aneurysm) [18]. However, ethnic differences in the location of the arterial dissection should be interpreted with caution, since Asian studies tend to use more intracranial vascular imaging tests, including HR-MRI, that enable the detection of a greater number of cases of intracranial dissection.
Moyamoya disease is an uncommon cerebrovascular disease that is characterized by progressive stenosis of the large intracranial arteries and a hazy network of basal collaterals. The main pathological changes in the stenotic segment in moyamoya disease include fibrocellular thickening of the intima, medial thinness, and a decrease in the outer diameter [19-22]. Regional differences in incidence and patient characteristics have been reported [23]. Moyamoya disease is more prevalent in East Asians than in Westerners. The population susceptible to moyamoya disease was estimated to be 16.16 million in East Asian countries [24]; however, the occurrence of moyamoya disease in Western countries has been increasingly reported [25].
It is often difficult to differentiate moyamoya disease from intracranial atherosclerosis in adult patients with ILAD. Unlike in childhood-onset moyamoya disease, distal internal carotid artery (ICA) involvement and moyamoya vessels may not be observed in the early phase of adult-onset moyamoya disease [26,27]. This suggests that the current criteria may have limitations for diagnosing adult-onset moyamoya disease. It was thought that moyamoya disease mostly occurs in children in Asia, and the hemorrhage rate is higher in adults than in children [28]. However, in contrast with previous reports, recent epidemiologic studies in Asians and Westerners revealed that patients with moyamoya disease are older (with peak age at 40s) and they have greater ischemia or are asymptomatic [25,29,30].
Vascular inflammatory disease, vasospasm, and immunological disorders are also important causes of non-atherosclerotic ILAD [9]. Vascular involvement is attributed to either direct damage of the endothelium or smooth muscle by pathogenic processes (e.g., infectious disease or vasculitis) or indirect damage resulting from accelerated atherosclerosis and endothelial dysfunction (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus or cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy [CADASIL]) [9].
Careful history taking and appropriate laboratory testing are essential. Bacterial or fungal infections and tuberculosis should be suspected, especially in developing countries, endemic areas, and immunocompromised patients. In systemic vasculitis, central nervous system involvement typically occurs several years after the onset of systemic involvement. Primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS) is a rare idiopathic vasculitis restricted to small leptomeningeal and parenchymal arteries and veins, without systemic involvement. Reversible vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS) is a clinical and radiologic syndrome characterized by acute onset, severe and recurrent headache, and reversible vasoconstriction of the cerebral arteries [31]. Headache is the most common symptom in both RCVS and PACNS. The characteristics of headache are different between the two disorders: thunderclap headache, the main presenting symptom of RCVS, is rare in PACNS [32]. Although the presence of typical luminal features is necessary for the diagnosis of RCVS (e.g., multifocal segmental vasoconstriction that normalizes within weeks) and vasculitis (e.g., alternating areas of stenosis and dilation), the initial angiogram can appear normal in some patients [33-35]. Characteristic wall changes on HR-MRI could help to differentiate these two conditions [36].
Luminal evaluation, such as catheter angiography, computed tomography angiography, and magnetic resonance angiography, is traditionally used to diagnose ILAD. Vessel wall imaging can depict the morphology of atherosclerotic plaques, arterial walls, and surrounding structures in the intracranial arteries, beyond simple luminal changes. In addition to intracranial atherosclerotic plaque, non-atherosclerotic pathological changes in the involved segment can be visualized with vessel wall imaging. For example, recent neuroimaging techniques, such as three-dimensional constructive interference in steady-state MRI and HR-MRI studies in patients with moyamoya disease, have demonstrated constrictive remodeling (e.g., narrowing of the arterial outer diameter) in affected segments, and concentric enhancement of the symptomatic segments, compatible with well-known pathological features of moyamoya disease [37-39]. A recent study conducted in the USA that included diverse ethnic groups, showed that vessel wall imaging using HR-MRI can significantly improve differentiation of the causes of ILAD when combined with luminal imaging [40]. In addition, the degree of enhancement on HR-MRI may be a marker for disease activity in non-atherosclerotic ILAD, including moyamoya disease and vasculitis [38,41,42]. At present, most studies use 3 Tesla (3T) MRI because it provides an image resolution sufficient to visualize structures inside the vessel wall. The recently introduced ultra-HR (7T) MRI has superior signal to noise and contrast-to-noise characteristics compared to 3T MRI, thereby providing a higher quality image [43-46]. This 7T MRI technique may even visualize vessel wall pathology in the absence of disease on conventional images. The imaging findings of intracranial plaques were validated with histopathology [43,47].
Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT, the light analog of IVUS) are intravascular imaging techniques used in interventional cardiology [48]. The results of several case reports suggest that these techniques may provide information for use in the selection of patients with intracranial atherosclerosis who may benefit from stent placement therapy [49]. These techniques could provide virtual histology to characterize the plaque in large intracranial vessels (distal ICA, VA, and basilar artery). An in vitro study using intracranial arterial segments with atherosclerotic plaques showed good correlation of virtual histology by IVUS and 7T MRI with histopathologic analysis [50]. However, these techniques require catheter angiography and were not studied in non-atherosclerotic ILAD.
Ongoing multinational GWASs will identify loci associated with specific stroke subtypes. However, GWASs in ischemic stroke are limited because of small sample sizes of patients with ILAD and of Asian populations where intracranial atherosclerosis is prevalent. A GWAS showed that certain genetic variants are associated with cervicocephalic dissection [51]. A brain-derived neurotropic factor gene polymorphism was reported to be associated with the severity of RCVS [52]. The presence of the ring finger protein 213 (RNF213) gene is associated with the greatest susceptibility to moyamoya disease in East Asians [53,54]. Several non-p.Arg4810Lys RNF213 variants were recently found in Caucasians and East and South Asian patients with moyamoya disease [54-57]. When trying to identify genetic polymorphism associated with intracranial atherosclerosis, it will be important to refine patient selection to avoid inclusion of non-atherosclerotic ILAD patients. Careful selection of intracranial atherosclerosis patients with the aforementioned neuroimaging techniques may be needed.
Several circulating blood biomarkers may be helpful in the identification of ILAD etiologies. For example, hyperhomocysteinemia and more recently, an elevated fibrillin-1 level (the release of an extracellular matrix glycoprotein by disruption of the medial layer), were reported in patients with cervicocephalic dissection [58-60]. On the contrary, caveolin-1 level was decreased in patients with moyamoya disease compared to those with intracranial atherosclerosis, suggesting that moyamoya disease is a caveolae (scaffolding proteins that are abundant in endothelial cells and are related to angiogenesis) disorder [61]. These protein levels may be related to the severity of vascular lesions [60]. Lastly, circulating genetic components, such as microRNAs, may play a role in the development of ILAD.
The current classification systems for stroke subtyping are largely based on luminal changes in large cervicocephalic vessels and the presence of potential sources of cardioembolism. Documentation of the pathophysiologic mechanisms underlying ILAD determines the proportion of intracranial atherosclerosis and other etiologic subtypes. Recently, ILAD of non-atherosclerotic origin has been increasingly recognized, especially in Asian populations. As shown in Figure 1, prospective observational HR-MRI studies in various study populations including non-stroke subjects [62], young-age stroke patients [63], and acute stroke patients [64], showed that non-atherosclerotic ILAD is prevalent across a wide range of atherosclerotic risk factors. Misclassification of ILAD of non-atherosclerotic origin as intracranial atherosclerosis could partly account for the high reported prevalence of intracranial atherosclerosis in Asians.
Unlike carotid dissection, the pathognomonic luminal findings of arterial dissection, i.e., the presence of an intimal flap and double lumen, are rarely observed in small intracranial arteries (with a mean luminal diameter ~3 mm), even with conventional angiography. Imaging of intracranial vessel walls with HR-MRI generally uses a resolution of <1 mm and the definite diagnosis of intracranial dissection often requires HR-MRI. A HR-MRI study demonstrated that almost two-thirds of intracranial dissection cases were misclassified as intracranial atherosclerosis using current luminal imaging techniques [64].
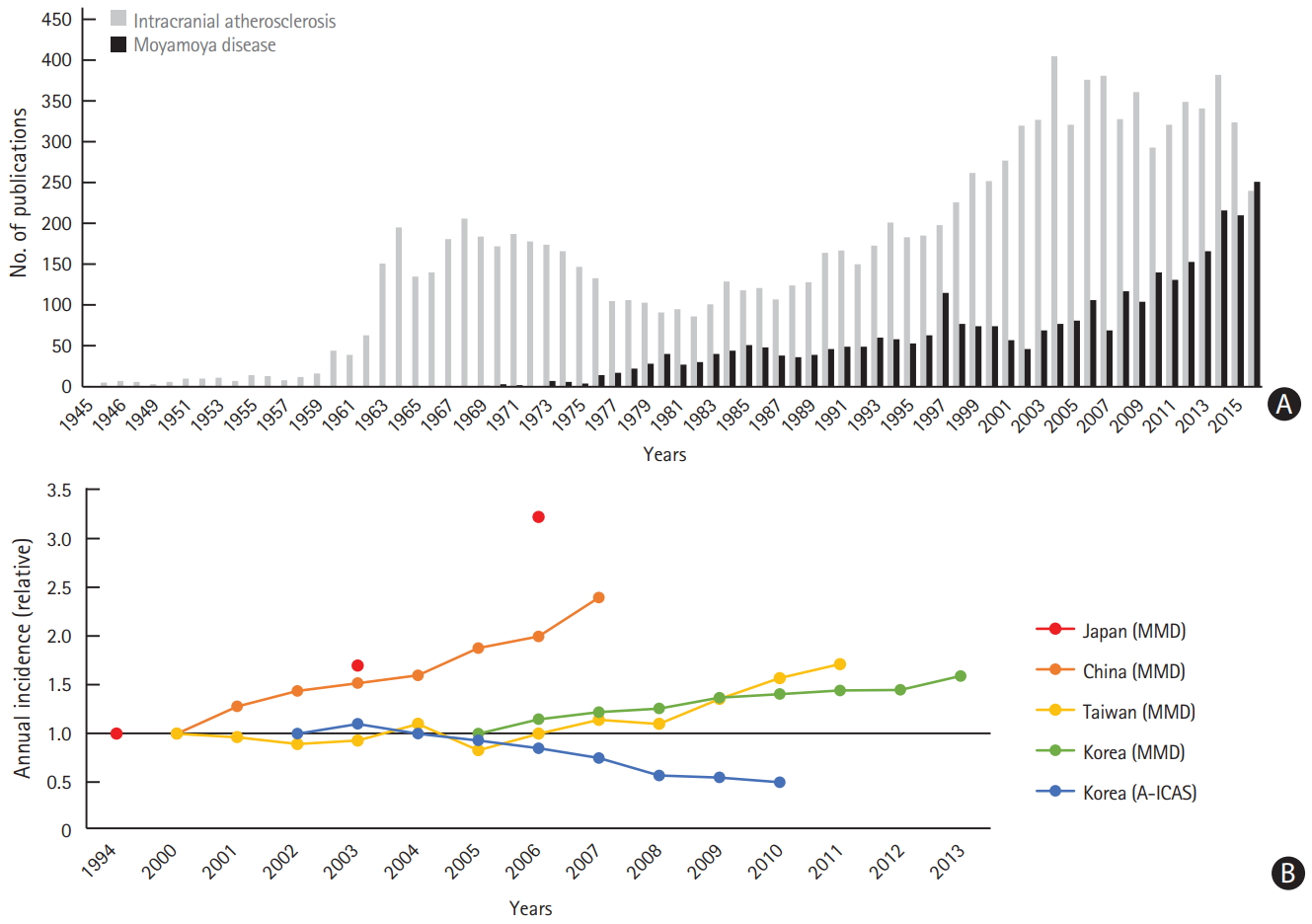
The annual incidence of moyamoya disease has reportedly increased in Japan, China, Taiwan, and Korea [65-68]. Such trends in the epidemiology of moyamoya disease may be accounted for by an increasing number of patients diagnosed with moyamoya disease rather than actual changes in the incidence of moyamoya disease. The recent interest in this disease could be the reason, as shown in Figure 2.
In contrast, nationwide, hospital-based data from Korea showed a decrease in the proportion of patients with intracranial atherosclerosis [69]. A recent pathologic study of 7,260 consecutive autopsy cases in Japan showed that the incidence and severity of intracranial atherosclerosis gradually decreased with later birth years over the last 50 years [70]. The authors suggest that this may be related to the development of therapeutic agents for the treatment of vascular risk factors and environmental changes.
With the increasing use of serial vascular imaging and HR-MRI, the discovery of new disease entities and the number of involved patients are expected to increase in the future. For example, RCVS was first named in 2007 [31], and it has been increasingly recognized in recent years, although it is still an underdiagnosed disease entity [71].
Risk factor control, aggressive medical management (including statins), and stent placement (in selected patients) are important for preventing stroke in patients with intracranial atherosclerosis [2,72-74]. However, therapeutic strategies used in intracranial atherosclerosis may not be helpful or may even be harmful in some patients with non-atherosclerotic ILAD.
The optimal treatment for patients with ischemic cerebrovascular disease due to intracranial dissection is unknown. The safety and effectiveness of thrombolysis or endovascular therapy for acute stroke and the choice of antithrombotic treatment (anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents) have not been assessed in randomized controlled trials [11,75]. Differentiation of intracranial dissection from intracranial atherosclerosis is important in young patients with ILAD, since the role of high-intensity statins in preventing stoke in intracranial dissection is unclear and unnecessary long-term use may cause complications.
The pathophysiology of moyamoya disease is still unknown, and there is no evidence that pharmacological therapy can stop or reverse its progression [76]. Several case series consistently showed that the role of stenting in moyamoya disease is highly questionable and it is associated with a high rate of symptomatic restenosis/occlusion [77-79]. Revascularization surgery remains the mainstay of treatment for moyamoya disease, whereas recent guidelines do not recommend bypass surgery for intracranial atherosclerosis [80].
Documentation of etiology is particularly important in ILAD associated with other causes. For example, immunosuppression is the mainstay of treatment in cases of vasculitis such as PACNS, but it has recently been reported that the use of steroids may contribute to worsening in patients with RCVS [81]. Use of HR-MRI enables RCVS to be differentiated from CNS vasculitis [82].
Non-atherosclerotic ILAD misclassified as intracranial atherosclerosis has many clinical implications. First, it may lead to incorrect conclusions from clinical studies examining risk factors or biomarkers of intracranial atherosclerosis. A recent HR-MRI study showed that the risk factor profile of patients with misclassified intracranial atherosclerosis (no typical luminal changes of dissection, but HR-MRI showed dissection and no plaque) was similar to that of patients with frank intracranial dissection on luminal imaging, but different from that of patients with intracranial atherosclerosis [64]. These misclassified patients may obscure the risk factors characteristic of intracranial atherosclerosis. Second, misclassification could adversely affect the results of clinical trials for intracranial atherosclerosis (involving antithrombotic, statin, or stent management). It is interesting that in younger patients with anterior circulation (in particular, 88% of intracranial ICA lesions, who might have progressive vasculopathy of moyamoya disease), Wingspan stent placement had a high in-stent restenosis rate [83]. Third, the natural course and mechanisms of stroke in patients with ILAD differ among different pathophysiologies of ILAD. While spontaneous recanalization can be expected during follow-up in intracranial dissection, vascular stenosis progresses in patients with moyamoya disease. In addition, most patients with intracranial atherosclerosis have recurrent ischemic stroke, but hemorrhagic stroke is relatively common in most non-atherosclerotic ILAD cases, such as intracranial dissection, RCVS, and moyamoya disease.
Nevertheless, it should be noted that non-atherosclerotic ILAD may trigger intracranial atherosclerosis, and vice versa. First, genetic factors for non-atherosclerotic ILAD may influence the development of intracranial atherosclerosis. The RNF213 genetic variant associated with moyamoya disease was also observed in Japanese and Korean patients with nonmoyamoya ILAD [84,85]. These results may in part explain the high prevalence of intracranial atherosclerosis in Asians. Patients with this variant may be prone to atherosclerosis. The RNF213 variant could lead to vascular fragility, which may render vessels more vulnerable to hemodynamic stress and secondary insults [86]. Second, stiff, rupture-prone vessels in patients with underlying intracranial atherosclerosis are also susceptible to minor trauma, resulting in intracranial dissection in the elderly. Similarly, intracranial dissection could trigger atherosclerotic changes, and patients with intracranial dissection may be prone to premature atherosclerosis.
With the application of new diagnostic techniques, the prevalence of non-atherosclerotic ILAD is expected to increase. Our review of the literature suggests that misclassification of nonatherosclerotic ILAD as intracranial atherosclerosis has clinical implications. More careful consideration of non-atherosclerotic causes and application of appropriate diagnostic techniques in patients with ILAD may not only provide better results in the treatment of patients, but it may also lead to more successful clinical trials for the treatment of intracranial atherosclerosis.
However, the application of new diagnostic techniques, such as HR-MRI, in ILAD patients has many limitations. First, HR-MRI sequences and techniques vary among studies. Optimal sequences and standardization to provide acceptable image quality and scanning time are needed. A collaborative international research network in China and North America (China-America MRI Plaque Imaging and Outcome Network [ChAMPION]) is ongoing. Second, routine application of the aforementioned diagnostic techniques is not possible in clinical practice. New diagnostic techniques may not be available, especially in low-income populations. Continuous efforts are needed to refine the approach to diagnosis of suspected non-atherosclerotic ILAD. For example, the use of HR-MRI could be considered in patients who are likely to have non-atherosclerotic ILAD, such as those with healthy risk factor profiles and no tandem stenotic lesions or calcification on luminal images. Lastly, in the area of extracranial large arteries such as carotid and coronary arteries, collecting arterial specimens from carotid endarterectomy provides a direct method to validate the capability of HR-MRI in identifying carotid plaque components. However, limited data on pathological correlation with in vivo MRI are available for ILAD, especially in non-atherosclerotic causes [87]. Further studies comparing MRI and histology are needed to validate the sensitivity and specificity of new diagnostic techniques in the differential diagnosis of ILAD. At the time of writing, we were aware of more than 10 active clinical trials on non-atherosclerotic ILAD (Supplementary Table 1). However, most trials involve a small number of patients and further studies with larger cohorts are warranted.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary materials related to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2018.00150.
Supplementary Table 1.
Ongoing clinical trials of patients with intracranial large artery disease, excluding interventional/surgery trials
Acknowledgments
Drs. Masatoshi Koga and Hiroharu Kataoka (National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center) provided useful advice.
This study was supported by grants of the Korea Health Technology R&D project (HC15C1056), the National Research Foundation of Korea (2018R1A2B2003489), an Intramural Research Fund for Cardiovascular Diseases of the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center, Japan (H28-4-1), and by a grant from the Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Korea (HI14C1985).
Figure 1.
Prevalence of intracranial large artery disease of non-atherosclerotic origin demonstrated by high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (HR-MRI) in (A) non-stroke subjects,[62] (B) young-age stroke patients,[63] and (C) acute stroke patients[64]. TIA, transient ischemic attack; PD, proton-density; Gd, gadolinium-enhancement. *Middle cerebral artery disease; † Excluding cases with typical luminal features of intracranial atherosclerosis (multiple tandem stenosis or carotid stenosis), moyamoya disease, or intracranial dissection; ‡ Both anterior and posterior circulation disease.
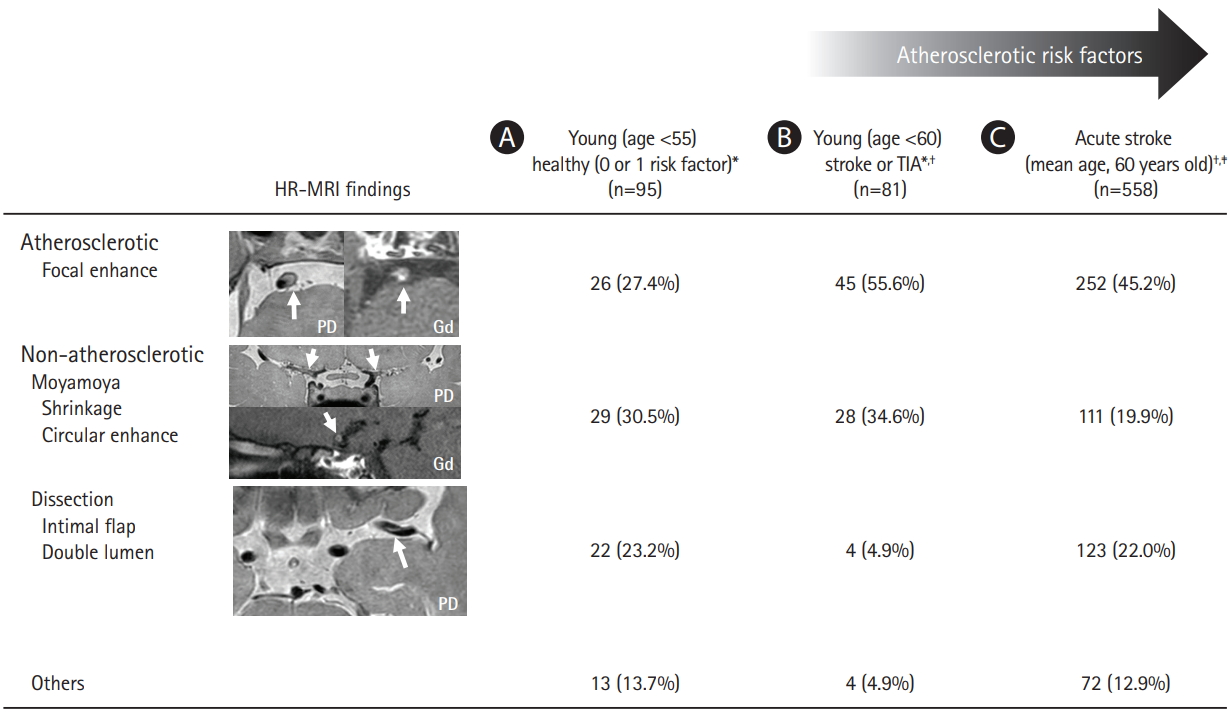
Figure 2.
Trends of moyamoya disease (MMD) and intracranial atherosclerosis in Korea. (A) Increase in the number of publications on MMD and (B) increasing annual incidence of patients diagnosed with MMD in East Asian countries (nationwide data), with a decrease in the proportion of patients with anterior circulation intracranial atherosclerosis (A-ICAS) (nationwide hospital-based data)[65]-69.
References
1. Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Howlett-Smith H, Stern BJ, Hertzberg VS, Frankel MR, et al. Comparison of warfarin and aspirin for symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis. N Engl J Med 2005;352:1305-1316.


2. Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Derdeyn CP, Turan TN, Fiorella D, Lane BF, et al. Stenting versus aggressive medical therapy for intracranial arterial stenosis. N Engl J Med 2011;365:993-1003.



3. Leung TW, Wang L, Soo YO, Ip VH, Chan AY, Au LW, et al. Evolution of intracranial atherosclerotic disease under modern medical therapy. Ann Neurol 2015;77:478-486.


4. Wong KS, Gao S, Chan YL, Hansberg T, Lam WW, Droste DW, et al. Mechanisms of acute cerebral infarctions in patients with middle cerebral artery stenosis: a diffusion-weighted imaging and microemboli monitoring study. Ann Neurol 2002;52:74-81.


5. Ryoo S, Lee MJ, Cha J, Jeon P, Bang OY. Differential vascular pathophysiologic types of intracranial atherosclerotic stroke: a high-resolution wall magnetic resonance imaging study. Stroke 2015;46:2815-2821.


6. Swartz RH, Bhuta SS, Farb RI, Agid R, Willinsky RA, Terbrugge KG, et al. Intracranial arterial wall imaging using high-resolution 3-tesla contrast-enhanced MRI. Neurology 2009;72:627-634.


7. Bodle JD, Feldmann E, Swartz RH, Rumboldt Z, Brown T, Turan TN. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging: an emerging tool for evaluating intracranial arterial disease. Stroke 2013;44:287-292.


8. Alexander MD, Yuan C, Rutman A, Tirschwell DL, Palagallo G, Gandhi D, et al. High-resolution intracranial vessel wall imaging: imaging beyond the lumen. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2016;87:589-597.



9. Kim JS, Caplan LR. Non-atherosclerotic intracranial arterial diseases. Front Neurol Neurosci 2016;40:179-203.


10. Biller J, Sacco RL, Albuquerque FC, Demaerschalk BM, Fayad P, Long PH, et al. Cervical arterial dissections and association with cervical manipulative therapy: a statement for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke 2014;45:3155-3174.


11. Debette S, Compter A, Labeyrie MA, Uyttenboogaart M, Metso TM, Majersik JJ, et al. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of intracranial artery dissection. Lancet Neurol 2015;14:640-654.


12. Sato S, Toyoda K, Matsuoka H, Okatsu H, Kasuya J, Takada T, et al. Isolated anterior cerebral artery territory infarction: dissection as an etiological mechanism. Cerebrovasc Dis 2010;29:170-177.


13. Schievink WI. Spontaneous dissection of the carotid and vertebral arteries. N Engl J Med 2001;344:898-906.


14. Kwon JY, Kim NY, Suh DC, Kang DW, Kwon SU, Kim JS. Intracranial and extracranial arterial dissection presenting with ischemic stroke: lesion location and stroke mechanism. J Neurol Sci 2015;358:371-376.


15. Guillon B, Lévy C, Bousser MG. Internal carotid artery dissection: an update. J Neurol Sci 1998;153:146-158.


16. Asaithambi G, Saravanapavan P, Rastogi V, Khan S, Bidari S, Khanna AY, et al. Isolated middle cerebral artery dissection: a systematic review. Int J Emerg Med 2014;7:44.




17. Kim BM, Kim SH, Kim DI, Shin YS, Suh SH, Kim DJ, et al. Outcomes and prognostic factors of intracranial unruptured vertebrobasilar artery dissection. Neurology 2011;76:1735-1741.


18. Krex D, König IR, Ziegler A, Schackert HK, Schackert G. Extended single nucleotide polymorphism and haplotype analysis of the elastin gene in Caucasians with intracranial aneurysms provides evidence for racially/ethnically based differences. Cerebrovasc Dis 2004;18:104-110.


19. Kuroda S, Houkin K. Moyamoya disease: current concepts and future perspectives. Lancet Neurol 2008;7:1056-1066.


20. Takagi Y, Kikuta K, Nozaki K, Hashimoto N. Histological features of middle cerebral arteries from patients treated for moyamoya disease. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2007;47:1-4.


21. Lin R, Xie Z, Zhang J, Xu H, Su H, Tan X, et al. Clinical and immunopathological features of moyamoya disease. PLoS One 2012;7:e36386.



22. Takagi Y, Kikuta K, Nozaki K, Fujimoto M, Hayashi J, Imamura H, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducing factor-1 alpha and endoglin in intimal hyperplasia of the middle cerebral artery of patients with moyamoya disease. Neurosurgery 2007;60:338-345.


23. Kleinloog R, Regli L, Rinkel GJ, Klijn CJ. Regional differences in incidence and patient characteristics of moyamoya disease: a systematic review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2012;83:531-536.


24. Liu W, Hitomi T, Kobayashi H, Harada KH, Koizumi A. Distribution of moyamoya disease susceptibility polymorphism p.R4810K in RNF213 in East and Southeast Asian populations. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2012;52:299-303.


25. Starke RM, Crowley RW, Maltenfort M, Jabbour PM, Gonzalez LF, Tjoumakaris SI, et al. Moyamoya disorder in the United States. Neurosurgery 2012;71:93-99.



26. Bang OY, Ryoo S, Kim SJ, Yoon CH, Cha J, Yeon JY, et al. Adult moyamoya disease: a burden of intracranial stenosis in East Asians? PLoS One 2015;10:e0130663.



27. Chung JW, Kim SJ, Bang OY, Kim KH, Ki CS, Jeon P, et al. Determinants of basal collaterals in moyamoya disease: clinical and genetic factors. Eur Neurol 2016;75:178-185.


28. Kim JS. Moyamoya disease: epidemiology, clinical features, and diagnosis. J Stroke 2016;18:2-11.




29. Baba T, Houkin K, Kuroda S. Novel epidemiological features of moyamoya disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2008;79:900-904.


31. Calabrese LH, Dodick DW, Schwedt TJ, Singhal AB. Narrative review: reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Ann Intern Med 2007;146:34-44.


32. Singhal AB, Topcuoglu MA, Fok JW, Kursun O, Nogueira RG, Frosch MP, et al. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes and primary angiitis of the central nervous system: clinical, imaging, and angiographic comparison. Ann Neurol 2016;79:882-894.


33. Hajj-Ali RA, Singhal AB, Benseler S, Molloy E, Calabrese LH. Primary angiitis of the CNS. Lancet Neurol 2011;10:561-572.


34. Lee MJ, Cha J, Choi HA, Woo SY, Kim S, Wang SJ, et al. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: implications for pathophysiology and diagnosis. Ann Neurol 2017;81:454-466.


35. Ducros A, Boukobza M, Porcher R, Sarov M, Valade D, Bousser MG. The clinical and radiological spectrum of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. A prospective series of 67 patients. Brain 2007;130(Pt 12):3091-3101.



36. Choi YJ, Jung SC, Lee DH. Vessel wall imaging of the intracranial and cervical carotid arteries. J Stroke 2015;17:238-255.




37. Kaku Y, Morioka M, Ohmori Y, Kawano T, Kai Y, Fukuoka H, et al. Outer-diameter narrowing of the internal carotid and middle cerebral arteries in moyamoya disease detected on 3D constructive interference in steady-state MR image: is arterial constrictive remodeling a major pathogenesis? Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2012;154:2151-2157.


38. Ryoo S, Cha J, Kim SJ, Choi JW, Ki CS, Kim KH, et al. Highresolution magnetic resonance wall imaging findings of moyamoya disease. Stroke 2014;45:2457-2460.


39. Yuan M, Liu ZQ, Wang ZQ, Li B, Xu LJ, Xiao XL. High-resolution MR imaging of the arterial wall in moyamoya disease. Neurosci Lett 2015;584:77-82.


40. Mossa-Basha M, Shibata DK, Hallam DK, de Havenon A, Hippe DS, Becker KJ, et al. Added value of vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging for differentiation of nonocclusive intracranial vasculopathies. Stroke 2017;48:3026-3033.



41. Wang M, Yang Y, Zhou F, Li M, Liu R, Guan M, et al. The contrast enhancement of intracranial arterial wall on high-resolution MRI and its clinical relevance in patients with moyamoya vasculopathy. Sci Rep 2017;7:44264.




42. Kuker W, Gaertner S, Nagele T, Dopfer C, Schoning M, Fiehler J, et al. Vessel wall contrast enhancement: a diagnostic sign of cerebral vasculitis. Cerebrovasc Dis 2008;26:23-29.



43. van der Kolk AG, Zwanenburg JJ, Brundel M, Biessels GJ, Visser F, Luijten PR, et al. Intracranial vessel wall imaging at 7.0-T MRI. Stroke 2011;42:2478-2484.


44. van der Kolk AG, Hendrikse J, Brundel M, Biessels GJ, Smit EJ, Visser F, et al. Multi-sequence whole-brain intracranial vessel wall imaging at 7.0 tesla. Eur Radiol 2013;23:2996-3004.


45. Wright PJ, Mougin OE, Totman JJ, Peters AM, Brookes MJ, Coxon R, et al. Water proton T1 measurements in brain tissue at 7, 3, and 1.5 T using IR-EPI, IR-TSE, and MPRAGE: results and optimization. MAGMA 2008;21:121-130.



46. Deng X, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Wang R, Ye X, et al. Comparison of 7.0- and 3.0-T MRI and MRA in ischemictype moyamoya disease: preliminary experience. J Neurosurg 2016;124:1716-1725.


47. Harteveld AA, Denswil NP, Siero JC, Zwanenburg JJ, Vink A, Pouran B, et al. Quantitative intracranial atherosclerotic plaque characterization at 7T MRI: an ex vivo study with histologic validation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2016;37:802-810.



48. Sanidas E, Dangas G. Evolution of intravascular assessment of coronary anatomy and physiology: from ultrasound imaging to optical and flow assessment. Eur J Clin Invest 2013;43:996-1008.


49. Pavlin-Premrl D, Sharma R, Campbell BCV, Mocco J, Opie NL, Oxley TJ. Advanced imaging of intracranial atherosclerosis: lessons from interventional cardiology. Front Neurol 2017;8:387.



50. Majidi S, Sein J, Watanabe M, Hassan AE, Van de Moortele PF, Suri MF, et al. Intracranial-derived atherosclerosis assessment: an in vitro comparison between virtual histology by intravascular ultrasonography, 7T MRI, and histopathologic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2013;34:2259-2264.



51. Debette S, Kamatani Y, Metso TM, Kloss M, Chauhan G, Engelter ST, et al. Common variation in PHACTR1 is associated with susceptibility to cervical artery dissection. Nat Genet 2015;47:78-83.



52. Chen SP, Fuh JL, Wang SJ, Tsai SJ, Hong CJ, Yang AC. Brainderived neurotrophic factor gene Val66Met polymorphism modulates reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. PLoS One 2011;6:e18024.



53. Kamada F, Aoki Y, Narisawa A, Abe Y, Komatsuzaki S, Kikuchi A, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies RNF213 as the first moyamoya disease gene. J Hum Genet 2011;56:34-40.



54. Liu W, Morito D, Takashima S, Mineharu Y, Kobayashi H, Hitomi T, et al. Identification of RNF213 as a susceptibility gene for moyamoya disease and its possible role in vascular development. PLoS One 2011;6:e22542.



55. Wu Z, Jiang H, Zhang L, Xu X, Zhang X, Kang Z, et al. Molecular analysis of RNF213 gene for moyamoya disease in the Chinese Han population. PLoS One 2012;7:e48179.



56. Cecchi AC, Guo D, Ren Z, Flynn K, Santos-Cortez RL, Leal SM, et al. RNF213 rare variants in an ethnically diverse population with moyamoya disease. Stroke 2014;45:3200-3207.



57. Ma J, Liu Y, Ma L, Huang S, Li H, You C. RNF213 polymorphism and moyamoya disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol India 2013;61:35-39.


58. Gallai V, Caso V, Paciaroni M, Cardaioli G, Arning E, Bottiglieri T, et al. Mild hyperhomocyst(e)inemia: a possible risk factor for cervical artery dissection. Stroke 2001;32:714-718.


59. Pezzini A, Del Zotto E, Archetti S, Negrini R, Bani P, Albertini A, et al. Plasma homocysteine concentration, C677T MTHFR genotype, and 844ins68bp CBS genotype in young adults with spontaneous cervical artery dissection and atherothrombotic stroke. Stroke 2002;33:664-669.


60. Zhu Z, Tang W, Ge L, Han X, Dong Q. The value of plasma fibrillin-1 level in patients with spontaneous cerebral artery dissection. Neurology 2018;90:e732-e737.


61. Bang OY, Chung JW, Kim SJ, Oh MJ, Kim SY, Cho YH, et al. Caveolin-1, ring finger protein 213, and endothelial function in moyamoya disease. Int J Stroke 2016;11:999-1008.


62. Ahn SH, Lee J, Kim YJ, Kwon SU, Lee D, Jung SC, et al. Isolated MCA disease in patients without significant atherosclerotic risk factors: a high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging study. Stroke 2015;46:697-703.


63. Kim YJ, Lee JK, Ahn SH, Kim BJ, Kang DW, Kim JS, et al. Nonatheroscleotic isolated middle cerebral artery disease may be early manifestation of moyamoya disease. Stroke 2016;47:2229-2235.


64. Park MS, Cha J, Chung JW, Seo WK, Kim GM, Bang OY. Arterial dissection as a cause of intracranial stenosis in East Asians. J Am Coll Cardiol 2017;70:2205-2206.


65. Kuriyama S, Kusaka Y, Fujimura M, Wakai K, Tamakoshi A, Hashimoto S, et al. Prevalence and clinicoepidemiological features of moyamoya disease in Japan: findings from a nationwide epidemiological survey. Stroke 2008;39:42-47.


66. Miao W, Zhao PL, Zhang YS, Liu HY, Chang Y, Ma J, et al. Epidemiological and clinical features of moyamoya disease in Nanjing, China. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2010;112:199-203.


67. Chen PC, Yang SH, Chien KL, Tsai IJ, Kuo MF. Epidemiology of moyamoya disease in Taiwan: a nationwide populationbased study. Stroke 2014;45:1258-1263.


68. Kim T, Lee H, Bang JS, Kwon OK, Hwang G, Oh CW. Epidemiology of moyamoya disease in Korea: based on National Health Insurance Service Data. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 2015;57:390-395.



69. Jung KH, Lee SH, Kim BJ, Yu KH, Hong KS, Lee BC, et al. Secular trends in ischemic stroke characteristics in a rapidly developed country: results from the Korean Stroke Registry Study (secular trends in Korean stroke). Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2012;5:327-334.


70. Kimura H, Takao M, Suzuki N, Kanemaru K, Mihara B, Murayama S. Pathologic study of intracranial large artery atherosclerosis in 7260 autopsy cases. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2017;26:2821-2827.


71. Chen SP, Fuh JL, Wang SJ. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: an under-recognized clinical emergency. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 2010;3:161-171.



72. Chaturvedi S, Turan TN, Lynn MJ, Kasner SE, Romano J, Cotsonis G, et al. Risk factor status and vascular events in patients with symptomatic intracranial stenosis. Neurology 2007;69:2063-2068.


73. Kim JS, Bang OY. Medical treatment of intracranial atherosclerosis: an update. J Stroke 2017;19:261-270.




74. Wabnitz A, Chimowitz M. Angioplasty, stenting and other potential treatments of atherosclerotic stenosis of the intracranial arteries: past, present and future. J Stroke 2017;19:271-276.




75. Toyoda K, Koga M, Hayakawa M, Yamagami H. Acute reperfusion therapy and stroke care in Asia after successful endovascular trials. Stroke 2015;46:1474-1481.


76. Bang OY, Fujimura M, Kim SK. The pathophysiology of moyamoya disease: an update. J Stroke 2016;18:12-20.




77. Natarajan SK, Karmon Y, Tawk RG, Hauck EF, Hopkins LN, Siddiqui AH, et al. Endovascular treatment of patients with intracranial stenosis with moyamoya-type collaterals. J Neurointerv Surg 2011;3:369-374.


78. Drazin D, Calayag M, Gifford E, Dalfino J, Yamamoto J, Boulos AS. Endovascular treatment for moyamoya disease in a Caucasian twin with angioplasty and Wingspan stent. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2009;111:913-917.


79. Khan N, Dodd R, Marks MP, Bell-Stephens T, Vavao J, Steinberg GK. Failure of primary percutaneous angioplasty and stenting in the prevention of ischemia in moyamoya angiopathy. Cerebrovasc Dis 2011;31:147-153.


80. Furie KL, Kasner SE, Adams RJ, Albers GW, Bush RL, Fagan SC, et al. Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke 2011;42:227-276.


81. Singhal AB, Topcuoglu MA. Glucocorticoid-associated worsening in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Neurology 2017;88:228-236.



82. Mandell DM, Matouk CC, Farb RI, Krings T, Agid R, terBrugge K, et al. Vessel wall MRI to differentiate between reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome and central nervous system vasculitis: preliminary results. Stroke 2012;43:860-862.


83. Turk AS, Levy EI, Albuquerque FC, Pride GL Jr, Woo H, Welch BG, et al. Influence of patient age and stenosis location on wingspan in-stent restenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008;29:23-27.



84. Miyawaki S, Imai H, Shimizu M, Yagi S, Ono H, Mukasa A, et al. Genetic variant RNF213 c.14576G>A in various phenotypes of intracranial major artery stenosis/occlusion. Stroke 2013;44:2894-2897.


85. Bang OY, Chung JW, Cha J, Lee MJ, Yeon JY, Ki CS, et al. A polymorphism in RNF213 is a susceptibility gene for intracranial atherosclerosis. PLoS One 2016;11:e0156607.



- TOOLS